Research article
Environmental Management Policies, Practices and Compliance with National and International Standards in The Eastern Industrial Park, Dukem Town, Ethiopia
- Bekele Girma Ayele 1*
College of Urban Development and Engineering Ethiopian Civil Service University, Ethiopia.
*Corresponding Author: Bekele Girma Ayele, College of Urban Development and Engineering Ethiopian Civil Service University, Ethiopia.
Citation: Bekele G. Ayele. (2024). Environmental Management Policies, Practices and Compliance with National and International Standards in The Eastern Industrial Park, Dukem Town, Ethiopia, Pollution and Community Health Effects, BioRes Scientia Publishers. 2(1):1-11. DOI: 10.59657/2993-5776.brs.24.014
Copyright: © 2024 Bekele Girma Ayele, this is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Received: January 22, 2024 | Accepted: February 06, 2024 | Published: February 17, 2024
Abstract
An environmental policy is a written statement describing an organization’s mission in relation to environmental impacts of its operational activities. However, many industries of developing country fail to implement their environmental policy. The problem also manifested in certain Industrial parks of Ethiopia. Hence, this study intended to examine environmental management policies, practices and compliance in the Eastern Industrial Park of Dukem, Ethiopia. The study used qualitative approach using both primary and secondary data. On the otherhand, purposive sampling was used to take the required sample. The target population of this study was the informants of selected government sectors and industries of Eastern Industrial Park. Structured interview question was designed to the informants. The qualitative data was analysed using thematic analysis. Tables, figures and charts were used for data presentation. Although industries in the industrial park had their own company environmental policy, however, there was limitation in documenting and implementing their environmental policy in their environmental management activities of the companies. The companies designedtheir policy merely to fulfil their requirement to the concerned authority. The findings revealed, the selected industries of Industrial Park not only fail to implement their policies but also limited in implementing the government and other international policies.
Keywords: environmental management policies; practices and compliance; national and international standards
Introduction: Background of the Study
Policy is a road map or guideline for future activities while policy statement is the intent of the government or organization to do something about certain issues. These include legislative statutes, administrative rules and regulations statements, executive orders and decrees, and speeches by public officials demonstrating the government's intentions and goals and what will be made to realize them (Nill and Kemp, 2009). On the other hand, an environmental policy is a written statement describing an organization’s mission in relation to the management of the environmental impacts of its operational activities (Persson and Runhaar, 2018). Environmental policies aimed to safeguard and sustainably use our natural environment. Intentionally or not, certain of these policies cause structural change. For instance, carbon prices shift investments from fossil fuels to renewable energy. Other environmental policies mainly promote process innovations and in so doing have only slight effects on structural change, such as new pollution control technology develops in existing factories (Altenburg & Assmann, 2017). In other way, Altenburg & Assmann (2017) described, green industrial policy as incorporating any government measure intended to speed up the structural change towards a low-carbon, resource-efficient economy in a way that also allows productivity improvements in the economy. As climate change mitigation and other ecological challenges gradually influence the future way of economic development, environmental concerns is a main part of industrial policymaking. However, implementation of environmental policy in most industries of developing country is the neglected part. This problem also exhibited in most industries of Ethiopia.
Statement of the problem
Industrial parks are developed for the purpose of industrial and associated facilities, business and service activities. Through categorizing industrial companies in a specific site, industrial parks present mutual and efficiency advantage (Avis, 2018). On the other hand, Eco-Industry focuses on industrial shift from industry emphasizing on conventional products, to function-oriented and process-closed industry, through combination of production, consumption, transportation, reduction and regulation (Thorpe, 1999). Conversely, as industrial parks help to social development and economic growth, parks can also bring negative environmental and social effects which include environmental pollution, resource reduction and human health deficiencies (Avis, 2018). When these issues are coupled by local challenges such as regional water scarcity, the problem of handling an industrial park becomes more complicated assignment (UNEP, 1997). According to Geng & Hengxin (2009), industrial parks also cause pollution of surface and groundwater due to industrial effluents. Besides, it also causes air pollution that harm human health. Policy of Environmental management at park level is, therefore, need attention in controlling and mitigating such harmful impacts.
On the other hand, Hamner (1997) and Yap (2000) recognized the current legal directives encourage companies to separately tackle environmental management by employing different environmental policies. According to Chen and Bacareza (1995), these policies are useful, predominantly when employed in combination with comparatively new strategies like market based economic instruments such as charges, taxes and subsidies to prevent local environmental problems. However, due to lack of policyimplementation most of industries in the developing countries are polluting the environment and impairing human health. These problems are also manifested in the Eastern Industrial Park of Dukem town, Ethiopia. According to Dukem town Environmental, Forest and Climate Change Authority (2021), due to limitation of environmental policy implementation, most of the companies in the Eastern Industrial Park were polluting the surrounding environment and affecting human health through emitting, particularly, air pollutants. Therefore, this study aimed in examining environmental management policies, practices and compliance with national and international standards.
Research objective
To examine environmental management policies, practices and compliance with national and international standards
Scope of the Study
The study was designed in the Easter Industrial Zone of Dukem town. The industrial companies which were regarded for this study include East Steal Company, Zong shun Cement Company, Dong Fang Textile Company, Diyuan Ceramics Company, Linde Garment Company, Lida Textile Company, and TY Wood Company. Key informants in the selected government sectors and selected industries were the population of the study. It was proposed to examine environmental management policies, practices and compliance with national and international standards. In conducting this, the researcher used cross sectional data.
Material and Methods
Study Area
The study is positioned in Dukem town Eastern Industrial Park, where it is engulfed in the North West by Galan town, in the South West by a peasant association of Akaki Wereda and in the South East bordered by Bishoftu town. The town is located at a distance of 37Km from the capital city, Addis Ababa. The entire area of the town is 9,630.3 ha. The GPS position of Dukem ranges 8o45’25” N to 8o50’30” N and 38o51’55” E to38o56’5” E. The climatic condition of the study area is, dominantly, semi temperate. The highest temperature of Dukem town is 29.3co during the month of March, April and May. Conversely, the lowest temperature is 7.1co during the month of August. The highest mean annual rainfall is 95mm while the lowest mean annual rain fall of the town is 48mm. According to Dukem town municipality, 2021, the population of the town was 58,017 (49.12 %) males and 56,010 (50.88 %) females which were entirely 114,027.
Data collection Method
Qualitative data from both primary and secondary data source was employed in the study. The primary data was gathered from the informants of selected government sectors and industries of Eastern Industrial Park using structured interview. On the other hand, secondary data was gathered from several sources such as Dukem town annual report, documented data in the companies, management plan, and environmental audit report of industrial companies.
Sampling Techniques and Size
Sampling techniques used in social sciences is an effort to describe several kinds of sampling approaches that are used in researches in an easy and clear manner (Alvi, 2016). In this study, cluster and purposive sampling were used to select the required sample.
Cluster sampling
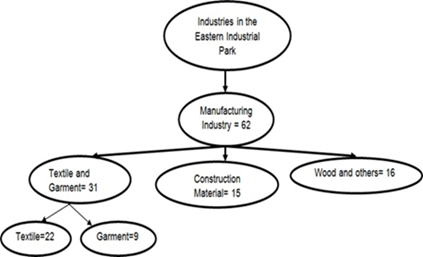
Cluster sampling is defined as where the whole population is categorized into groups or clusters (Taherdoost, 2016). In this study, cluster sampling was used to categorize industries in the industrial park based on their product types. Accordingly, industries in the park were classified as textile and garment product manufacturing, construction material product manufacturing, wood and others product manufacturing. Out of 62 industries that were operational 15 were construction materials, 16 were wood and other product, 31 were textile and garment manufacturing industries. The following Figure1 depicts the clustered industries in the Eastern Industry Park of Dukem town.
Figure 1: depicts the clustered industries in the Eastern IndustryPark of Dukemtown
Purposive sampling
Purposive sampling is a strategy in which specific settings, persons or events are chosen purposely in order to deliver important information that cannot be gained from other choices (Taherdoost, 2016). For this study purpose, out of 62 manufacturing industries seven of them werepurposely selected i.e. Di Yuan ceramics company, Dong Fang Textile Company,East steal metal company, Zhongshun Cement Company, Lida Textile Company, TY Wood Company and Linde Garment Company. This was due to theproblem aggravate more in theselected industries. In addition, purposive sampling was employed to select key informants from government sectors and selected industries from Eastern industrial park. This was done by taking sectors and departments that are working closely with industries, considering, that employees that were working in these sectors and departments and head of the government sector offices including the vice know well about environmental policy and practices in the industries of Eastern Industrial Park. Hence, experts and heads of the office from government sector such as Dukem town Investment, Land Administration, Labor and Social affairs, Environmental protection, Forest and Climate change Authority office were purposely selected as key informants.
Sample size determination
Under this section the sample size for qualitative part which was selected from government sectors and industries was presented. Accordingly, four key informants from each four government sectors such as Urban Land Administration, Investment, Environmental protection and Labor and social affairs offices were selected purposively which was a total of 16. On the other hand, five key informants from each seven manufacturing industries such as Ty wood Company, Diyuan Ceramics Company, East steel Company, Linde Garment Company, Zhongshun Cement Company, Dong Fang textile Company which was 35 in number. Hence, the total number of focal persons, department heads and heads of selected office and industries were 51 in number.
Data Analysis and Presentation
The qualitative data was analyzed using thematic analysis method while Tables, figures and charts were used for data presentation.
Ethical Consideration
The research carried out with the informants of sampled government sectors and industries was assisted by supporting letters from Ethiopian Civil Service University. The researcher collected data prudently to safeguard privacy of information, confidentiality and personal safety of the interviewees. Verbal permission was got from the interviewees. The candidates were told about the objective of the research before interviewing. Those who were willing to participate were interviewed with structured interview questions. The gathered data was checked for clarity, completeness and accuracy.
Results and Discussion
Under this section, environmental management policy, practices and compliance with the national and international standards were discussed.
Environmental policy practices of the companies
The selected industries of industrial park had their own policy which was incorporated in their environmental management plan. The selected industries had both policy statement and policy provision which states about environmental management in the companies.
Their environmental policy statement incorporated vital goals and principles that outlined the companies’ environmental commitments. The policy statement also provided a unifying vision of environmental principles and guidance to the companies’ corporate activities. Besides, environmental policy statement provided social and environmental responsibilities and lays foundation for guiding principles on which the companies operate their business in a sustainable manner (Linda, 2020; TY Wood, Dong fang, Zhongshun, Linde, East steel and Di Yuan, 2019). The companies intended to devote and improve environment as an expression of the companies’ owners guiding principles, and a demonstration of “thinking globally and act locally’’ sensibility. In order to follow the principles specified in the environmental policy, the companies intended to strive and ensure that all features of the companies’ activities to have least harmful effects on the environment by realizing the following environmental management policy provision:
• “…fully aware of all environmental legislations and ensure that regulatory requirements are met and, where feasible, improve upon.
• Monitoring the implementation of the company corporate policy by carrying out periodic audit of compliance and, when appropriate, introduce remedial measures.
• Ensure all employees, in the course of their duties, act in accordance with the company environmental policy.
• Encourage suppliers, contractors and venders to act in accordance with the company environmental standards.
• In addition, area of particular attention within the business will be assessed and due attention will be given to selection of non-polluting technology, waste minimization, reusing and recycling and the reduction of energy consumption.
• The company also makes a positive environment contribution in the local community by encouraging open communication, general environmental awareness and the promotion of community projects… (Linda, 2020; TY Wood, Dong fang, Zhongshun, Linde, East steel and Di Yuan, 2019”
As the companies’ environmental management plan revealed, the selected industries had their own company written environmental policy. However, their policy had incorporated within the companies’ environmental management plan which was designed to manage environmental issues in the companies. Although industries in the industrial park had their own company environmental policy, however, there was limitation in documenting and referring their environmental policy in their day-to-day activities of the companies. The researcher found their policy in the town Environmental, Forest and Climate Change Authority office. This in turn hindered them from implementing their environmental management policy regularly and reporting as per their policy guide line. Besides, it showed the companies poor commitment towards policy documentation and implementation of environmental management activities of the companies as per their policy in one hand and meeting the country’s sustainable development goal on the other hand. The companies designed their policy merely to fulfill their requirement to the concerned authority (Dukem Environment, Forest and Climate Change Authority (DEFCCA), 2021).
On the other hand, as key informants from selected industries of Industrial Park and selected government sector said, though the industries had written environmental policy, however, there was no community participation during the companies’ environmental policy preparation. Consequently, stakeholders’ interests were not represented in the environmental policy processes. However, active community involvement in the policy preparation and decision-making course will help local communities (Marzuki, 2008). Besides, despite the selected industries had environmental policy, however, its implementation in the industries were not fully coherent with national development policy because their policy implementation didn’t fully acknowledge the national development goals and its actions didn’t fully consistent with strategies and planning processes for the national development. According to Paul & Weinthal (2019) the CRG of Ethiopia is the commitment of the country towards building climate resilient green economy through using efficient technology and clean energy unlike industries of industrial park that have been using fossil fuel and coal for energy consumption and inefficient technology of communal treatment plant that has been releasing effluents without efficient treatment.
As interview was made with key informants of Dukem town Environment, Forest, Climate Change authority and document review revealed, the majority of selected industries started their operation without EIA preparation and approval. As result, the town environmental protection authority enforced them to design their own environmental management plan. Currently, the majority of industries in the industrial park had their own environmental management plan with poor implementation practices. However, according to Gillard & Wood (2003) having a sound environmental management plan in place can significantly advance both environmental performance and regulatory compatibility, and minimize the risk of occurrences, fines and punishments. As Companies mentioned in their environmental policy provision, they intended to make environmental inspection and audit regularly. However, the sampled companies with the exception of Di Yuan Ceramics they didn’t have even environmentalists who inspect internally the issues of environment regularly in the companies. Nevertheless, the Federal Environmental Protection Authority of Ethiopia regulation 159/2008a industrial companies are obliged in planning and applying internal environmental inspection techniques and keeping written records of the contaminants generated and the disposal techniques.
Besides, over the past three years, environmental audit in selected industries have been made once by local Environmental protection authorities. Likewise, the selected industries have been inspected by public environmental authorities such as federal and state environmental protection bureau once. However, in doing so, the local, regional and federal authority have been selecting and inspecting industries with high environmental and social impact. The remaining industries with less environmental impact have not been given any consideration to inspect and audit the environmental pollution that generate from the industries. This indicates that there was no regular inspection and environmental auditing, particularly, by federal and state environmental protection bureaus. Besides, the policy provisions that were intended in the companies’ environmental policy, practically, they were not applicable in the companies’ environmental management practices. However, by applying an environmental audit program, companies can detect the likely future problems (Stanwick and Stanwick, 2001). Besides, the significance of an environmental audit comprises improved compliance management, training aid to instruct the employees, and an instrument for public dealings (Bae & Seol 2006). In addition, it revealed that, the companies had not only problem of regular inspection and environmental auditing but also certain industries that deemed with less environmental problem had not been inspected and made their environmental audit by federal and state environmental protection bureaus. In contrast to these facts, as the selected industries management plan review revealed, the companies expected to make regular inspection and audit both by internal and external concerned agencies. Besides, in all industries there need to be regular inspection and implementation of environmental audit. However, as Laplante & Rilstone (1996) proved both inspections and the threat of an inspection have a strong adverse effect on pollution emissions. Besides, inspections also encourage more regular reporting from the industry. Moreover, inspection is required to satisfy government regulation, guarantee quality parameter is met by the companies (Afrinaldi & Pratama, 2020).
On the other hand, as field survey (2020) indicated, though companies mentioned to establish environmental, health and safety department, however, each selected industries in the Eastern Industrial Park had no their companies environmental or health and safety department or unit which safeguard the human health and environment from deterioration. Conversely, the EIZ (East Industry Zone) department that made inadequate support and follows up on the issue of environment in the companies. This reveals that each companies had no its own health and safety department that runs environmental issues and employee’s safety. However, an effective environmental and safety department not only guarantees the environment but also minimizes costs, and improves productivity (Koehn & Datta, 2003). In addition, with the exception of Di Yuan Ceramics Company, each of the other selected industries in the industrial park had no environmentalist or skilled experts that run the issues of environment in the companies, however, only the manager who was concerned with the matter of environmental management in each company (DEFCCA, 2020). This shows that each companies had no their own expert who has knowledge and skill about environmental management in the industries and this made solving the issues of environment in the companies a difficult task. Nevertheless, this comprises not only failing to achieve aims and objectives in staffing but also in sustaining service provision excellence and securing companies success particularly in the environmental management in the industrial companies (Kueblboeck & Stander, 2016).
As interview made with key informants of government sector showed, concerning environmental management practices that have been made in the selected companies, there were poor practices in the industries in order to implement environmental management plan in the companies. These were manifested as most of these companies haven’t concerned about environmental issues, they have given more emphasis on profit /business making in their companies i.e. the issue of environment was neglected part. However, AlKhidir & Zailani (2009) confirmed environmental issues become stronger and more widespread. In this concern, businesses essential to place equal balance both on the environment and their business aims. Besides, although the sampled industries from Industrial Park have environmental management plan, they have not implemented as per the national and regional standard and they also didn’t submit their companies’ environmental performance report to the concerned authority regularly. On the other hand, as Wheeler & Elkington (2001) explained communicating effectively with different authorizes and stakeholders on improvement towards environmental quality are an important condition of companies’ responsibility. In addition, companies’ environmental performance reporters were revealed to have a commonly higher level of acceptance (Martin & Hadley, 2008). The following Figure 2 depicts interview made with key informants of government sector.
Figure 2: Interview made with key informants of government sector about their Environmental policy practices
Source: photo captured by the author
Furthermore, though the companies’ environmental policies intended to safeguard the environment, there were poor management practices of solid waste in the companies. As the selected textile and garment industries have been selling their majority of solid waste after collecting and putting in the sack and storing wastes in the temporary site which was not well designed and the rest selected companies have been collecting the solid waste and dumping in the town disposal site after storing for a short time in the temporary site which is not properly designed in the industrial park compound. This was degrading the environment in one hand and affecting the health of people on the other hand. However, Solid Waste Management proclamation no. 513/2007 of Ethiopia intends to promote community involvement to prevent adverse impacts and improve benefits that obtained from solid waste. Accordingly, any person shall collect wastes that pollute the environment in a specifically chosen location and in a manner, which does not affect the health of the society. Furthermore, the proclamation obliged not to dispose liquid, solid or any other waste in a manner which pollute the environment or affects the health of local community.
Likewise, there were also poor liquid waste management practices in contrast to what was mentioned in their policy provision. The liquid waste that has been generated from textile and other selected industries and which has been treated below the national standards utilized by local farmers for irrigation purposes after passing through the communal treatment plant of Eastern Industrial Park. However, regulation 159/2008a of the Federal Environmental Protection Authority of Ethiopia, intended to prevent industrial pollution and promote compatibility of industrial development with environmental protection. A company subject to the regulations is obliged to prevent or minimize the production and discharge of industrial pollutants to the level not beyond the environmental standards.
On the other hand, the selected industries of industrial park haven’t implemented an environmental management system such as EMAS, ISO 14001 and others for their industrial environmental management performance that made them capable to acquire different certification. This revealed that, the companies were poor in using international environmental management system which made them get international recognition and certification in one hand and improving environmental quality performance in another hand. Besides, EMS was not requirement in the selected industries. However, Massoud, et.al, (2010) confirmed, the fact that EMS such as EMAS, ISO 14001 and others is not a legal requirement create the most salient features hindering the implementation of the standard. On the other hand, poorly imposed environmental laws will not guarantee environmental advancement (Massoud et al., 2010). The following Table 1 presents summary of the Environmental policy practices of the companies and its implications on environmental management processes of the industries.
Table1: Summary of Environmental policy practices of the companies and its implications on environmental management processes of the industries.
| Name of the industry | The existence institutional provision for environmental management | The presence of EMS (ISO) as per guideline | The presence of solid waste management system, if ‘yes’ what is the technique used | The presence of liquid waste management system, if ‘yes’ what is the technique used | Sufficient budgetary provision | Staff sufficiency and their capacity | ||||||
| Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | Yes | No | |
| Dong fang spinning, printing and Dyeing textile manufacturing | √ | √ | √ Storing in the temporary waste disposal site Selling the small cuts of cloths Disposing in the town solid waste disposal site | √ Reusing Treating in the primary and communal treatment plant | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Lida Textile Manufacturing | √ | √ | // | // | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Linde Garment Manufacturing | √ | √ | // | There is no liquid waste | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Ty wood Manufacturing | √ | √ | √ Reusing cuts of wood as a source of energy for boiler plant | √ Reusing wastes Treating waste | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Diyuan Ceramics Manufacturing | √ | √ | √ Reusing broken and damaged ceramics | √ Reusing liquid waste Treating liquid waste | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| East steel manufacturing | √ | √ | √ Reusing and recycling of scrap metal and cuts of metal | √ Reusing liquid waste Treating liquid waste | √ | √ | √ | |||||
| Zhongshun Cement Manufacturing | √ | √ | Collecting and disposing cartoon | √ Reusing liquid waste Treating liquid waste | √ | √ | √ | |||||
Environmental management policy practices and compliance with the national and international standards
Under this topic, the environmental policy practices of the selected companies and its compliance with the national and international standards were described. The sampled companies had environmental policy and management plan, practically, there were limitation of implementation. What was stated in the document was not applicable in the companies, particularly, in the waste management and emission control practices (DEFCCA, 2021). According to proclamation N0 177/2005 of Oromia Regional State Environmental Protection Authority describes, industries that discharge emission to the environment expected to design environmental management plan document that intended to minimize or alleviate pollution by expert that has competency of knowledge and skill from Federal Environmental Protection Authority and apply it as per the designed documents. However, though the companies had environmental management pan, practically, they hadn’t been implementing it. In other side, the majority of selected industries from the industrial park got license from federal government and started working before preparing their EIA documents. However, as to Environmental Impact Assessment Proclamation No. 299/2002 of Ethiopia states, industries obliged to prepare EIA and got permission from Environmental management authority before starting their operation. Accordingly, the proponent of the project must prepare the EIA documents according to the format identified in the legislation. The EPA will assess the EIA and either accept the project or reject it. The Proclamation also needs specified kinds of projects to be open to an EIA and obtain an authorization from the EPA or the relevant regional environmental agency before starting the operation of the project.
Besides, in the selected companies of industrial park, there was no continuous supervision and follow up from the regional and federal protection authority (DEFCCA, 2021). This indicates that there was limitation of continues environmental supervision and follow up. The national government law which was formulated to be implemented in the industrial park was not implemented in the selected industries of industrial park. In contrast, Proclamation No. 886/2015 states the regional and federal environmental laws of Ethiopia shall implement within industrial parks. Besides, the Ministry of Environment and Forest shall open an office within industrial parks for the implementation, protection, supervision, and application of environmental standards, norms, safeguards, mitigation plans and management within the Industrial Parks. Though the sampled industries had environmental policy and management plan, environmental pollution from industrial park has been increasing. Currently, there was air pollution since sampled industries such as Dong Fang textile industry using coal, charcoal and diesel for energy consumption; Di Yuan ceramic industry utilizing gas oil for energy consumption. On the other hand, the majority of textile industries in the industrial park, they were using chemicals for coloring that harm the health of human in the dyeing process. Hence, liquid waste discharges polluted the environment, particularly, water and soil. Besides, there was no well-designed temporary site in the compound for solid waste disposal (DEFCCA, 2021).
This has been polluting the environment particularly through releasing bad smell and contaminating the environment which in turn affect the health of local people. However, according to Ethiopian Constitution, article 44 grants all citizens the right to reside in a clean and healthy environment. Moreover, Proclamation No. 300/2002, article 3 (1), instructs that, “No person shall pollute or cause any other person to pollute the environment by violating the relevant environmental standard”. On the other hand, article 3 (2) of the same proclamation additionally states that the relevant regional environmental agency could take legal or administrative actions against a person who violate law and discharges any pollutant into the environment. Further, Proclamation No. 300/2002 intends to safeguard the right of citizens to a healthy environment and to force duties to safeguard the environment of the country. Moreover, the law intended to address the management of hazardous waste and preparation of environmental quality standards for water, air, soil and pollution monitoring. This implies that companies not only had limitation of implementing the country environmental policy but also had limitation in implementing their own environmental policies. However, there were measures undertaken by the town and regional Environment, Forest and Climate Change Authorities on the selected company such as Di Yuan Ceramics as the company was using Coal as a source of energy that polluted the environment and for the non-compliances to the standards. Besides, there was complains from the local community repeatedly that initiated the local and regional authority to shut the company for couple of days (DEFCCA, 2021). Though there was government corrective action, there was still limitation in taking measures as per regulatory framework. The measures that are stated in the federal and regional legal frameworks were not implemented when companies violate and pollute the environment.
Summary of the finding
Under this section, the summary of the finding, conclusion and recommendation of the paper were also presented.
Summary of the finding
Although industries in the industrial park had their own company environmental policy, however, there was limitation in documenting and referring their environmental policy in their day-to-day activities of the companies. The companies designed their policy merely to fulfil their requirement to the concerned authority (Dukem Environment, Forest and Climate Change Authority (DEFCCA), 2021). Currently, the majority of industries in the industrial park had their own environmental management plan with poor implementation practices. As Companies mentioned in their environmental policy provision, they intended to make environmental inspection and audit regularly. However, the sampled companies with the exception of Di Yuan Ceramics Company they didn’t have even environmentalists who inspect internally the issues of environment regularly in the companies. However, according to Federal Environmental Protection Authority of Ethiopia regulation 159/2008a industrial operators are obliged in designing and implementing internal environmental inspection methods and keeping written records of the pollutants produced and the disposal mechanisms. In addition, it revealed that, the companies had not only problem of regular inspection and environmental auditing but also certain industries that deemed with less environmental problem had not been inspected and made their environmental audit by federal and state environmental protection bureaus. In contrast to these facts, as the selected industries management plan review revealed, the companies intended to make regular inspection and audit both by internal and external concerned agencies. Besides, industries designed to make regular inspection and environmental audit; however, practically they were not effective in implementation. According to Laplante & Rilstone (1996) proved both inspections and the threat of an inspection have a strong adverse effect on pollution emissions. Besides, inspections also encourage more regular reporting from the industry. Moreover, inspection is required to satisfy government regulation, guarantee quality parameter is met by the companies (Afrinaldi & Pratama, 2020).
As interview made with key informants of government sector showed, concerning environmental management practices that have been made in the selected companies, there were poor practices in the industries in order to implement environmental management plan in the companies. These were manifested as most of these companies haven’t concerned about environmental issues, they have been giving more emphasis on profit /business making in their companies i.e., the issue of environment was neglected part. However, AlKhidir & Zailani (2009) confirmed that environmental issues become stronger and more widespread. In this concern, businesses essential have equal balance both on the environment and their business. Besides, although the sampled industries from Industrial Park have environmental management plan, they have not implemented as per the national and regional standard and they also didn’t submit their companies’ environmental performance report to the concerned authority regularly. However, as Wheeler & Elkington (2001) explained communicating effectively with different authorities and stakeholders on improvement towards environmental quality are an important condition of companies’ responsibility. Furthermore, though the companies’ environmental policies intended to safeguard the environment, there were poor management practices of solid, liquid and gaseous waste in the companies. On the other hand, the selected industries of industrial park haven’t implemented an environmental management system such as EMAS, ISO 14001 and others for their industrial environmental management performance that made them capable to acquire different certification. This revealed that, the companies were poor in using international environmental management system which made them get international recognition and certification in one hand and improving environmental quality performance in another hand. Besides, EMS was not requirement in the selected industries. However, Massoud et.al (2010) confirmed, the fact that EMS such as EMAS, ISO 14001 and others is not a legal requirement create the most salient features hindering the implementation of the standards. On the other hand, poorly imposed environmental laws will not guarantee environmental advancement without the implementation of EMS (Massoud et al.).
The sampled companies had environmental policy and management plan, practically, there were limitation of implementation. What was stated in the document was not applicable in the companies, particularly, in the waste management and emission control practices (DEFCCA, 2021). However, according to Oromia Regional State Environmental protection proclamation N0 177/2005 states, industries that discharge emission to the environment expected to prepare environmental management plan document that intended to minimize or mitigate pollution by expert that has competency of knowledge and skill from Federal Environmental Protection Authority and implement it as per the designed documents. Besides, in the selected companies of industrial park, there was no continuous supervision and follow up from the regional and federal protection authority (DEFCCA, 2021). This indicates that there was limitation of continues environmental supervision and follow up. The national government law which was formulated to be implemented in the industrial park was not implemented in the selected industries of industrial park. In contrast, Proclamation No. 886/2015 states the regional and federal environmental laws shall implement within industrial parks. Besides, the Ministry of Environment and Forest shall open an office within industrial parks for the implementation, protection, supervision, and application of environmental standards, norms, safeguards, mitigation plans and management within the Industrial Parks.
Conclusion
In general, the selected industries of Industrial Park not only fail to implement their policies but also limited in implementing the government and other international policies. Besides, there was noncompliance of existing environmental management policy practices in the companies with the national and international standard. Hence, this study is potentially important so that local and national government engage in enforcing the implementation of industrial park policies and working on compliance of the companies’ environmental policy with national and international standard.
Recommendation
Based on the main finding of the study, the following recommendation forwarded: There should be sub-national and national government involvement in the implementation of industrial park policies that formulated to protect the environment in general and human health in particular.
Since there was no effective implementation of environmental management policy practices in the selected companies of Eastern Industrial Park, there should be regular inspection, monitoring and follow up by the internal and external organs. The existing different regulatory frameworks that were associated with pollution control in the companies of Eastern Industrial Park need to be implemented. There would be regulatory measure on the industrial companies that violate the standard set by legal, and degrade the environment and the incompliance of industrial companies’ environmental policy practices with other national and international standards.
Declarations
Acknowledgements
Not applicable
Authors' contributions
Bekele Girma conducted the study including data gathering, analysis, interpretation and other research activities.
Funding
Not applicable
Availability of data and materials
The interview result and secondary data used in the current study are available from the corresponding author.
Competing interests
The author declares that he has no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study has been commented and approved by Environment and Climate Change department of Ethiopian Civil Service University, College of Urban Development and Engineering.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
References
- Afrinaldi, F. & Pratama, H. B. (2020). Selecting the best quality inspection alternative based on the quality, economic and environmental considerations. Quality Management Journal, 28(1):2-16.
Publisher | Google Scholor - AlKhidir, T, & Zailani, S. (2009). Going green in supply chain towards environmental sustainability. Global Journal of Environmental Research, 3(3):246-251.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Alvi, M. (2016). A manual for selecting sampling techniques in research.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Bae, S. & Seol, I. (2006). An exploratory empirical investigation of environmental audit programs in S&P 500 companies. Management Research News.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Chen, X., & Bacareza, L. B. (1995). Application of economic and regulatory instruments for environmental management in Asian industrializing countries. Industry and Environment, 18(4):16-20.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Di Yuan Ceramics Plc (2019). Environmental Management Audit report. Eastern Industry Park, Dukem, Ethiopia.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Dong Fang Manufacturing Plc (2019). Environmental and Social Management Plan. Eastern Industry Park, Dukem, Ethiopia.
Publisher | Google Scholor - East Steel Metal Manufacturing Plc (2021). Environmental Management Audit report. Eastern Industry Park, Dukem, Ethiopia.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Geng, Y. & Hengxin, Z. (2009). Industrial Park management in the Chinese environment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 17(14):1289-1294.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Gillard, C. F. & Wood, B. (2003). Boosting environmental performance... reducing regulatory noncompliance: to rectify poor environmental performance, seek to identify the root causes of failure, and then implement a comprehensive Environmental Management System (EMS). (Feature Report). Chemical Engineering, 110(3):58-65.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Hamner, B. (1997). Industrial Ecology in East Asia. Journal of Industrial Ecology, 1(4):6-8.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Koehn, E. E. & Datta, N. K. (2003). Quality, environmental, and health and safety management systems for construction engineering. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 129(5):562-569.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kueblboeck, S. & Standar, M. (2016). Experts lack in the hospitality industry: An empirical study of the hotel industry in the Braunschweig-Wolfsburg region. Zeitschrift für Tourismuswissenschaft, 8(2):285-317.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Laplante, B. & Rilstone, P. (1996). Environmental inspections and emissions of the pulp and paper industry in Quebec. Journal of Environmental Economics and management, 31(1):19-36.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Lida textile Manufacturing Plc (2019). Environmental and Social Management Plan. Eastern Industry Park, Dukem, Ethiopia.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Martin, A. D. & Hadley, D. J. (2008). Corporate environmental non‐reporting–a UK FTSE 350 perspective. Business Strategy and the Environment, 17(4):245-259.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Marzuki, A. (2008). Decision making and community participation: A case study of the tourism industry in Langkawi. Tourism: An International Interdisciplinary Journal, 56(3):227-241.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Massoud, M. A. Fayad, R., Kamleh, R. & El-Fadel, M. (2010). Environmental management system (ISO 14001) certification in developing countries: challenges and implementation strategies.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Paul, C. J., & Weinthal, E. (2019). The development of Ethiopia's Climate Resilient Green Economy 2011–2014: implications for rural adaptation. Climate and Development, 11(3):193-202
Publisher | Google Scholor - Stanwick, P. and Stanwick, D. (2001), “Cut your risks with environmental auditing”, The Journal of Corporate Accounting and Finance, 12(4):11-14.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Taherdoost, H. (2016). Sampling methods in research methodology; how to choose a sampling technique for research. How to Choose a Sampling Technique for Research.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Thorpe, B. (1999). Citizen's guide to clean production. University of Massachusetts, Lowell Center for Sustainable Production.
Publisher | Google Scholor - TY Wood Manufacturing Plc (2019). Environmental and Social Management Plan. Eastern Industry Park, Dukem, Ethiopia.
Publisher | Google Scholor - UNEP. (1989). Basel Convention on the control of transboundary movements of hazardous wastes and their disposal.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Wheeler, D. & Elkington, J. (2001). The end of the corporate environmental report? Or the advent of cybernetic sustainability reporting and communication. Business strategy and the environment, 10(1):1-14.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Yap, N. T. (2000). Who says command-and-control doesn't work? POLICY OPTIONS- MONTREAL-, 21(3):65-70.
Publisher | Google Scholor