Review Article
Surgical Approaches to Ovariohysterectomy in the Bitch: A Review
- Amanawit Kasa
- Haregawi Tesfaye *
School of Veterinary Medicine, Jimma University, Ethiopia.
*Corresponding Author: Haregawi Tesfaye, School of Veterinary Medicine, Jimma University, Ethiopia.
Citation: Tesfaye H, Kasa A. (2023). Surgical Approaches to Ovariohysterectomy in the Bitch: A Review. Clinical Case Reports and Studies, BioRes Scientia Publishers. 3(4):1-11. DOI: 10.59657/2837-2565.brs.23.078
Copyright: © 2023 Haregawi Tesfaye, this is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Received: October 04, 2023 | Accepted: October 18, 2023 | Published: October 25, 2023
Abstract
Ovariohysterectomy in dogs, also called spaying, is a surgical removal of the ovaries along with the womb of a female dog, to make it disable to have any more conception. It is a very common elective surgery in dogs in the United States. Current reports from the American Society for Prevention of Cruelty against Animals indicated that 83% female dogs are neutered. There are two ways in which a spay is usually performed. These are traditional and laparoscopically methods. The primary goal of this seminar is to conduct a review of surgical approaches to ovariohysterectomy in dogs and explaining its role in dog population control and reduction of Zoonotic disease. The main indications are population control, prevention of diseases for the reproductive tract and elimination of undesirable behaviors associated with hormonal cycling but contraindicated in the case of a hypothermia, dehydration, and mydriasis. According to reports, the incidence of surgical complications of canine OVH varies between 6.1 and 27.0%. The major complications are hemorrhage, ovarian remnant syndrome, stump pyometra, adhesions, and wound dehiscence or infection, as well as anesthetic complications and drug reactions. As a result, postsurgical complications should be managed accordingly for good prognosis besides government of the country have to implement dog registration and certification rules and regulations. This surgical method should be considered for controlling dog over population and public health importance.
Keywords: surgery; ovary; Ovariohysterectomy
Introduction
Ovariohysterectomy in dogs, also known as spaying, is a surgical ablation of the ovaries along with the uterus of a female dog, to make it disable to have any more conception (Slatter, 2003). Ovariohysterectomy is the most common surgical technique in small animal surgery performed in some countries and is unethical or illegal in other countries It is a very common elective surgery in dogs in the United States. Current reports from the American Society for Prevention of Cruelty against Animals indicated that 83
Literature Review
Gonadectomy in females included both ovariectomy and ovariohysterectomy surgical methods, and recent review showed the related short- and long-term risks and benefits of gonadectomy of dogs (Hart, 2001). According to genetic predisposition, gonadal hormones appear to mainly influence the pathogenesis of mammary tumors (Overley et al., 2005). On this basis ovariohysterectomy is considered a prophylactic and therapeutic effect on average better health and reduced mortality rate than intact, and it is still recommended to avoid high population densities, animal suffering and the spread of zoonoses (Reichler, 2009).
Indications and Contraindications of Ovariohysterectomy
Elective sterilization of pet dogs is a common surgical procedure performed in veterinary practice. The main benefit of sterilization is population control and the reduction in euthanasia of unwanted dogs (kutzler,2020). This operation is indicated to avoid heat (estrus) cycles, prevent pregnancy, remove diseased or cancerous female reproductive organs and markedly decrease the risk of acquired diseases of the female reproductive system. The spay operation essentially removes the possibility of a severe infection of the uterus (pyometra) (Hagman,2012). Ovarian and uterus excision is the treatment of choice for ovarian teratomas in canine (Blaszak et al., 2009), particularly in cases presenting secondary pyometra (Arlt and Haimerl ,2016). Naturally occurring disease may be more common in females because one infected male often mates with numerous females; single Canine transmissible venereal tumor affected male dog spread the disease to 11 of 12 females (Rebbeck et al., 2009). Neutering also reduces the risk of biting in certain breeds of dogs (Casey et al., 2014) and increases lifespan by 26.3% compared to intact bitches (Hoffman et al., 2013). There are contraindications to the Ovariohysterectomy such as if the bitch presents with a generalized condition with hypothermia, dehydration, and mydriasis. Similarly, animals presenting with hepatorenal insufficiency should not undergo general anesthesia if the urea levels are greater than 0.6 g/L and the creatinine is greater than 10 mg/L, such animals are associated with poor per and postoperative survival (Djemil et al., 2009).
Ovariohysterectomy Benefits
The control of dog populations is a practice carried out on a global scale by means of different methods that have been classified in general as surgical (sterilization) and non-surgical (immune-sterilization, hormonal control, isolation, intrauterine device) (Munoz et al., 2011). Like many African countries, the rate of urbanization in Ethiopia is increasing rapidly and closely linked with human and dog populations. Therefore, understanding of pet’s populations and associated ownership characteristics of these expanding urban communities remains a high priority (Gsell et al., 2012). Despite this presumably large number of dog and cat populations and the burden of zoonotic diseases in Ethiopia, research on determinants of their ownership as well as non-ownership is absent (Gebremedhin et al., 2020). The primary benefit of neutering is the prevention of unintended reproduction. Though the number of unwanted cats and dogs euthanized at animal shelters in the United States has decreased from an estimated 23.4 million in 1970 to about 4.5 million by the year 2000 (Clancy and Rowan, 2003). Canine ovariohysterectomy (OVH) is one of the most frequently used surgical procedures in the case of companion animals (Howe, 2006). It is recommended by many animal welfare organizations to control dog populations, and is recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a means of population control for dogs, as part of rabies control programs in endemic areas (WHO, 2004).
Spaying is conducted for elective sterilization of female dogs to control over population of dogs there by preventing inter and intra species disease transmissions (Asrat and Melkamu 2018). Dogs transmit several viral and bacterial diseases to humans. Zoonotic diseases can be transmitted to human by infected saliva, aerosols, contaminated urine or feces and direct contact with the dog. Viral infections such as rabies and norovirus and bacterial infections including Pasteurella, Salmonella, Brucella, Yersiniaenterocolitica, Campylobacter, Bordetella bronchiseptica, Coxiella burnetii, Leptospira, Staphylococcus intermedius and Methicillin resistance staphylococcus aureus are the most common viral and bacterial zoonotic infections transmitted to humans by dog (Ghasemzadeh and Namazi, 2015). The main parasitic zoonoses in Europe related to dogs and cats, are Toxoplasmosis, leishmaniosis, giardiosis, echinococcosis, dirofilariosis and toxocariosis (baneth et al., 2016). These diseases are potential risks which can be eliminated by neutering the bitches (Robertson, 2008). OVH is the treatment of choice for most uterine diseases, including: congenital anomalies, pyometra, localized or diffuse cystic endometrial hyperplasia (CEH), uterine torsion, uterine prolapse, uterine rupture, and uterine neoplasia .It is also indicated for treatment of ovarian tumors, (non-responsive to medical treatment), to prevent recurrence of vaginal hyperplasia, to prevent hormonal changes that can interfere with medical therapy in patients with endocrine diseases and to eliminate the transfer of inherited diseases (Slatter, 2003).
Surgical sterilization is advantageous over chemical or hormonal immunization as it provides lifelong reproductive control and may also reduce problematic behaviors such as some forms of aggression or the propensity for specific dogs to roam (Raymond., 2015). Dog bite injury risk is an aspect of dog behavior that has substantial societal and public health implications. It causes an estimated 580,000 human injuries and an average of 20 human deaths in the US per year, with 51% of reported dog bite cases occurring in children under age 12 (Waters et al., 2011). Consequently, a considerable body of literature based on dog bite injury report data exists, some of which also includes the effects of desexing (Simpson et al., 2019). A systematic literature review based on observational studies of dog bite risk concluded that five out of six of the articles considered showed that intact dogs were more likely than desexed dogs to cause bite injuries (Van Meervenne et al., 2019).
Anatomy of Reproductive Organs of the Bitch
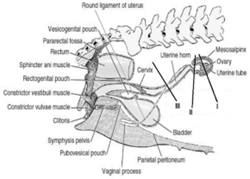
Ovaries are located about halfway between the last rib and the crest of the ileum, ventral to the fourth lumber vertebra, and adjacent to the caudal pole of the corresponding kidney. The bursa entirely encloses the ovary, which is connected to the cranial end of the uterine horn by the ovarian ligament, which is also the ovary's suspensory ligament (Asrat and melkamu, 2018). The ovarian artery and vein give blood to the ovaries. The uterus has unusually long narrow horns and a very short body. The anterior portion of the vagina is linked to a broad ligament (Concannon and Meyers-Wallen, 1991). With the exception of the vagina, which is situated in the pelvis, the genital organs of the bitch are mostly found in the abdominal cavity. The body of the uterus, which measures 3-5 cm in length in the intrabdominal position and starts from the anterior straight of the pelvis then divides into two divergent horns after a few centimeters, lies on the floor of the abdomen on either side of the lineaalba, then travels back up towards the ova. The neck of the uterus is relatively short, measuring 1- 2 cm long, and it lies a few centimeters in front of the anterior border of the pubis. The right and left uterine arteries provide the uterus with blood. The uterine branch of the ovarian artery irrigates the part of the uterus that is closest to the oviduct, while the uterine branch of the vaginal artery supplies the neck and the rest of the body (Bojrab, 1998).
Figure 1: The location of the genitals in bitches Source Murphy et al., Evans and de lahunta, 2012.
Preoperative Surgery Diagnosis
The dog will need to be fasting (no food or water) the night before surgery and the day of surgery. Prior to anesthesia, blood should be tested to ensure its organs are functioning properly and undiagnosed diseases are absent from the blood work. A pre-anesthetic, pain medication, and antibiotic are administered by injection to the dog (Akhmad et al., 2021). Surgical site infections (SSIs) are a recognized risk of any surgical procedure in veterinary medicine. One of the keys to prevention of SSIs is reducing exposure of the surgical site to endogenous and exogenous microbes, beginning in the preoperative period (Anderson et al., 2013). Depending on veterinarian’s protocols and the bitch health status tests and diagnostics that can be performed by complete blood cell count, chemistry profile, radiograph of the chest, urinalysis, PCV and TP. These steps are very important for checking dog’s blood cells to determine presence of infection, any issues with the liver, kidneys, clotting factors, and if there are any tumors or abnormalities present within the body. Age is not always a factor unless a veterinarian wants to avoid the first estrus (heat) cycle (Overley et al., 2005). A pre-existing fluid deficit should be corrected prior to the administration of anesthetic agents in order to support the patient’s ability to tolerate the impending cardiopulmonary depressant effects experienced during general anesthesia (Tivers and Baines, 2010).
Different Surgical approaches of ovariohysterectomy
There are two ways in which a spay is usually performed. These are Traditional and laparoscopically methods (Howe et al., 2006).
Laparoscopic Surgery
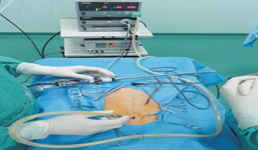
In veterinary medicine the first laparoscopic procedure was performed in 1985, sterilization of a bitch by ligation of the uterine horns (Wildt and Lavler,1985). In small animals the surgical procedures that can be performed using laparoscopy are abdominal organs biopsy, gastropexy, feeding tube placement, ovariectomy and laparoscopic assisted ovariohysterectomy and cryptorchidectomy (Lhermete and Sobel, 2008). Due to minor tissue injury, laparoscopic surgery, as a minimal invasive procedure is thought to reduce the neuroendocrine, immunologic and metabolic response of the organism compared to laparotomic surgery (Freeman, 1999). Laparoscopic surgery consists of the veterinarian making two to three small incision sites on the abdomen followed by using carbon dioxide gas to inflate and extend the abdominal area (Lansdowne et al.,2012). Then using laparoscopes, the veterinarian can visualize the reproductive tract. The blood vessels are ligated using clips, suture, or vessel-sealing devices, and the tools are used to grasp and manipulate the reproductive organs. This approach is popular because it’s less traumatic than a traditional spay, however, it is much more expensive and takes a longer time to perform.
Figure 2: Laparoscopic ovariohysterectomy in a bitch. source karadjole et al., 2012.
Traditional
There are two approaches that can be performed for hysterectomy in bitches. These include flank (side between ribs and hips) and midline (Louis et al., 2012).
Flank Approach Position
The lateral flank approach has been described for both dogs and cats in a number of references (Levy,2004). The skin incision for the lateral flank approach should be made in a dorsoventral direction, taking care to avoid superficial vessels located near the ventral aspect of the flank. The subcutaneous tissue should be incised using a combination of blunt and sharp dissection. The abdominal wall should be identified and entered via a grid approach using a hemostat or Car malt forceps to bluntly dissect through the separate layers of the abdominal oblique muscles. It is important to grasp the transverse abdominis muscle with thumb forceps to maintain control of the body wall. The uterine horn should then be grasped with thumb forceps and delivered through the incision. The suspensory ligament should be broken down and the ovary delivered through the incision. The broad ligament is then punctured with a clamp to grasp the suture material and a ligature is placed in the ovarian pedicle as close as possible to the lumbar wall (McGrath et al., 2004). The right ovarian pedicle should double ligated with 2-0 chromic catgut, have to severed using three clamp technique and is released after inspection for hemorrhage (Murugesan et al.,2020). The procedure is repeated for left ovarian pedicle. The uterine body is exteriorized and an encircling ligature with 2-0 chromic catgut is placed cranial to cervix, the uterine body severed by using three clamp technique and released after inspection for hemorrhage. The peritoneum, transverse and internal oblique muscles should be closed in a continuous lock stitch suture pattern with 2-0 chromic catgut and external oblique muscle can be closed in a horizontal suture pattern (Murugesan et al.,2020). If the subcutaneous connective tissue is very abundant, a simple continuous subcutaneous suture is performed. The skin is preferably sutured with cross matters suture pattern with non-absorbable suture materials (Djemil Bencharif, 2010).
Midline approach
The Bich is placed in dorsal recumbency. A midline or slightly paramedian incision is made through the Linea alba or rectus abdominis muscles and parietal peritoneum to enter the peritoneal cavity. The procedure is then identical to that described for the flank approach. The uterus is identified by repelling the intestine cranially and the bladder caudally and grasped with atraumatic forceps. The incision is extended if necessary. Then, abdominal incision can be closed, the Linea alba and subcutaneous tissues are closed with chromic cat gut (Allahdin et al., 2022).
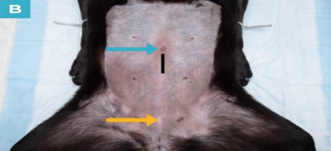
Figure 3: Midline incision placement and length in a bitch.
Incision area (black line), umbilicus (blue arrow) and cranial brim of the pubis (yellow arrow). source Jacob et al., 2020.
Comparison Right Lateral Flank and Ventral Midline Approach
The length of incision and duration of surgery in ventral midline approach is higher when we compare to right flank. On the basis of merits and demerits of two surgical ways, it can be concluded that the right lateral flank side can be a good option to the commonly used ventral midline approach for ovariohysterectomy in dog. Advantages of the flank approach to ovariohysterectomy include the ability to remotely view the surgical wound and reduced risk of evisceration in the event of wound dehiscence than mid-ventral (Levy, 2004; Arunkumar et al., 2017).
Procedure of Ovariohysterectomy
Ovariohysterectomy procedure traditional method can be performed and the other alternative is laparoscopic spaying (Rosewell, 2016). The dog will feel drowsy from the pre anesthetic/sedative, but mask gas anesthesia will likely follow to allow the dog to rest comfortably. The anesthetized patient is placed on the surgical table in dorsal recumbency (on the back). The hind legs are tied cranially for stabilization purposes. The patient will have the hair clipped close to the skin in a section from the xyphoid to the pubis, an inch past the nipples. The freshly clipped area will then be scrubbed for surgery. A drape is placed on top of the dog, creating a sterile field. The drape is clamped in place and an opening is made in the drape, just above the focus point of the surgery. An incision is made using a scalpel blade, typically created over the midline just caudal to the umbilicus. The incision will pass through the subcutaneous tissues, fat and eventually, the peritoneal cavity. The uterus is located using a hook, similar to a crochet hook. The uterine horn will be gently pulled through the incision opening and a Kelly forceps will be used to grasp the reproductive organ. The uterus is dissected and tied off with 0 or 2-0 monofilament absorbent sutures, which won’t require removal. Several sutures will be placed to ensure closure (Greenberg et al.,2010). The excess tissues from the pedicle are removed and inspected for bleeding. If no bleeding is present the uterine pedicle is placed back into the peritoneal cavity. The peritoneum, muscle and subcutaneous tissue should close using simple continuous suture with cat-gut 1-0 and the skin have to closed by applying horizontal mattress sutures with silk thread (Talukder et al.,2021).
Post Operative Care of Ovariohysterectomy
Strict monitoring is important in Ovariohysterectomy dog should not be allowed off the leash for seven to 14 days after surgery and can be prevented from licking the incision, running, jumping, and climbing stairs. Outdoor dogs should be kept inside for two weeks. The incision should be checked daily for any signs of swelling, redness, or heat. Elizabethan collars are routinely recommended by veterinarians, most commonly to prevent dogs from removing their sutures following surgery. Elizabethan collars are designed to prevent the animal from reaching the incision area by their mouths (Smith, 2015). Oxygenation essential if the surgical shock is extremely great. The animal is warmed, especially if the female was in poor condition before the procedure, it should be rolled in a blanket and placed at a heated kennel. IV fluid therapy is run with isotonic saline along with an injection of vitamin, k and corticosteroids. The sutures can be removed after 10 days. Any stagnant uterine secretions in the cervix and vagina must eliminated within the times following so cease complete. If female dog is in heat (estrus) at the time of surgery, it is a requirement to remain them aloof from un-neutered males for a minimum of two weeks. If a male tries to mate together with her serious bleeding and trauma to the reproductive tract may occur, possibly leading to death (Salmeri et al., 1991). The operative site should be checked for swelling or discharge and thus the operative incision should be dressed with antiseptics. The patient should receive antibiotics and analgesics for seven and three days respectively as well as diet should incline for the first 63 days and the patient should be observed for proper urination and defecation. Cutaneous sutures should be removed after 8-10 days of operation or after complete healing (Concannon and Meyers-Wallen, 1991).
Post Operative Complication of Ovariohysterectomy
According to reports, the incidence of surgical complications of canine OVH varies between 6.1 and 27.0%, without correlation with the age of the animal, the skills of the surgeon, or the presence of a reproductive disease (Burrow et al., 2005). The major complications are hemorrhage, ovarian remnant syndrome, stump pyometra, adhesions, and wound dehiscence or infection, as well as anesthetic complications and drug reactions (Adin, 2011). Most dogs are extremely tolerant of pain and show no signs of discomfort from the procedure. Unfortunately, as a result, they will attempt to resume their normal level of activity immediately after surgery, and this puts them at risk for complications. Elective OVH has been reported to increase the risk of occurrence of tumor such as transitional cell carcinoma, osteosarcoma and hemangiosarcoma (Kustritz, 2007) as well as increase the risk of occurrence of orthopedic disorders such as hip dysplasia and cranial cruciate ligament rupture (Hart et al., 2014). Other complications of ovariohysterectomy include obesity, urinary tract disorders, diabetes mellitus and hypothyroidism (Angioletti et al., 2004; Lund et al., 2006).
Table 1: Surgery Related Complications After Ovariohysterectomy
| Complications | Body wt. in Kg | % Of occurrence | Site of the complication |
| Intraabdominal Hemorrhage | < 25> | 2% (7/290) | Abdominal cavity |
| >25 | 79% (69/87) | ||
| Vaginal Bleeding | <25> | 2% (2/8) | Vagina |
| >25 | 15% (11/72) | ||
| Ligation of the Ureter | <25> | 2% (2/109) | ovarian pedicle |
| >25 | 3% (3/109) | uterine stump | |
| Ovarian Remnant Syndrome | <25> | 43% (47/109) | ovarian pedicle |
| >25 | 17% (12/72) | uterine stump | |
| Stump Granuloma | <25> | 60% (12/20) | ovarian pedicle |
| >25 | 20% (4/20) | uterine stump |
Source Reviewed from van et al., 2006.
Conclusion
Ovariohysterectomy is a surgical procedure that involve removal of uterus and ovary. It is indicated when the bitches are encountered with various reproductive tract pathological conditions, dystocia, and undesirable sexual behaviors. However, it is contraindicated during hypothermia, dehydration, and mydriasis. It is also important to induce irreversible sterilization of female dogs, thereby controlling the overpopulation of dogs and hence preventing disease transmission among different species of animals and human beings. However,
Recommendations
Based on the above conclusions, the following recommendations are forwarded: The government must to create legislation requiring dog registration and certification, For the purpose of managing the overpopulation of dogs and preventing Zoonosis, ovarian hysterectomy in females should be regarded as essential. Post-surgical complications should be managed accordingly for good prognosis.
Abbreviations
< Less than
> Greater than
IV Intravenous
Kg kilogram
OVH Ovariohysterectomy
PCV Packed cell volume
TP Total protein
WHO world health organization
wt weight
References
- Adin, C.A., (2011). Complications of ovariohysterectomy and orchiectomy in companion animals. Veterinary Clinics: Small Animal Practice, 41(5):1023-1039.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Ajadi, T.A., Makinde, F.A., Adebayo, O.O. and Adeleye, A.I. (2018). Incidence, indication and prognosis of ovariohysterectomy in dogs in Abeokuta, Nigeria. Sokoto Journal of Veterinary Sciences, 16(2):47-53.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Akhmad, H., Sari, D.K. and Deniati, S. (2021). Management of Mammae Tumor Cases in Mixed Chow Dog Breeds at Makassar Zoo Clinic. Jurnal Riset Veteriner Indonesia (Journal of The Indonesian Veterinary Research).
Publisher | Google Scholor - Akinrinmade, J.F. and Eyarefe, O.D. (2012). Enterologic and gynaecologic complications of ovariohysterectomy in the bitch. Nigerian Veterinary Journal, 33(3).
Publisher | Google Scholor - Allahdin, A., Tabatabaei-Naeini, A., Bigham-Sadegh, A. and Safavi-Naeini, K., (2022). Evaluation of Two Different Ovariohysterectomy Approaches on Alpha-1-Acid Glycoprotein (AGP) Level in Cats. Iranian Journal of Veterinary Surgery, 17(1):44-49.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Anderson, M.E., Foster, B.A. and Weese, J.S. (2013). Observational study of patient and surgeon preoperative preparation in ten companion animal clinics in Ontario, Canada. BMC veterinary research, 9(1):1-11.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Angioletti, A., De Francesco, I., Vergottini, M. and Battocchio, M.L. (2004). Urinary incontinence after spaying in the bitch: incidence and oestrogen-therapy. Veterinary Research Communications, 28(1):153-155.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Arlt, S.P. and Haimerl, P., (2016). Cystic ovaries and ovarian neoplasia in the female dog–a systematic review. Reproduction in Domestic Animals, 51:3-11.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Arunkumar, S. (2017). Comparison of right flank and ventral midline approach for ovariohysterectomy in dogs.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Asrat Mulat and Melkamu Samrawit., (2018).Review on Ovariohysterectomy: Surgical approach, Postoperative Complications and their Management in Bitches. International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Research. 5(3):2393-8870
Publisher | Google Scholor - Baneth, G., Thamsborg, S.M., Otranto, D., Guillot, J., Blaga, R., et al. (2016). Major parasitic zoonoses associated with dogs and cats in Europe. Journal of comparative pathology, 155(1):S54-S74.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Belanger, J.M., Bellumori, T.P., Bannasch, D.L., Famula, T.R. and Oberbauer, A.M., (2017). Correlation of neuter status and expression of heritable disorders. Canine genetics and epidemiology, 4(1):1-12.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Blaszak, B., Walkowski, M., Ibbs, M. and Jaskowski, J.M. (2009). Teratoma adultum in a bitch: a case report. Veterinární medicína, 54(8):379-381.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Bojrab, M., 1998. Currient techniques in small animal surgery/Bojrab M. New York: Baltimore.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Burrow, R., Batchelor, D. and Cripps, P. (2005). Complications observed during and after ovariohysterectomy of 142 bitches at a veterinary teaching hospital. Veterinary Record, 157(26):829-833.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Casey, R.A., Loftus, B., Bolster, C., Richards, G.J. and Blackwell, E.J. (2014). Human directed aggression in domestic dogs (Canis familiaris): Occurrence in different contexts and risk factors. Applied Animal Behaviour Science, 152:52-63.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Clancy, E.A. and Rowan, A.N. (2003). Companion animal demographics in the United States: A historical perspective.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Concannon, P.W. and Meyers-Wallen, V.N. (1991). Current and proposed methods for contraception and termination of pregnancy in dogs and cats. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association, 198(7):1214-1225.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Diesel, G., Brodbelt, D. and Laurence, C. (2010). Survey of veterinary practice policies and opinions on neutering dogs. Veterinary Record, 166(15):455-458.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Djemil B., Lamia A., Annabelle G., and Daniel T. (2010). Department of Reproductive Pathology, ONIRIS:Nantes-Atlantic National College of Veterinary Medicine. Food Science and Engineering.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Djemil Bencharif, Lamia Amirat, Annabelle Garand, and Daniel Tainturier. (2009). Review Article of Ovariohysterectomy in the Bitch. Department of Reproductive Pathology, France
Publisher | Google Scholor - Downes, M., Canty, M.J. and More, S.J. (2009). Demography of the pet dog and cat population on the island of Ireland and human factors influencing pet ownership. Preventive veterinary medicine, 92(1-2):140-149.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Egenvall, A.G.N.E.T.A., Hedhammar, Å., Bonnett, B.N. and Olson, P. (1999). Survey of the Swedish dog population: age, gender, breed, location and enrolment in animal insurance. Acta veterinaria scandinavica, 40(3):231-240.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Freeman, L.J. (1999). Veterinary endosurgery. Mosby. St. Louis. IX - XVI.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Gebremedhin, E.Z., Sarba, E.J., Getaneh, A.M., Tola, G.K., Endale, S.S. et al. (2020). Demography and determinants of dog and cat ownership in three towns of West Shoa zone, Oromia Region, Ethiopia. BMC veterinary research, 16(1):1-12.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Ghasemzadeh, I. and Namazi, S.H., (2015). Review of bacterial and viral zoonotic infections transmitted by dogs. Journal of medicine and life, 8(4):1.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Gsell, A.S., Knobel, D.L., Cleaveland, S., Kazwala, R.R., Vounatsou, P. et al. (2012). Domestic dog demographic structure and dynamics relevant to rabies control planning in urban areas in Africa: the case of Iringa, Tanzania. BMC veterinary research, 8(1):1-10.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Hagman, R. (2012). Clinical and molecular characteristics of pyometra in female dogs. Reproduction in domestic animals, 47:323-325.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Hart, B.L. (2001). Effect of gonadectomy on subsequent development of age-related cognitive impairment in dogs. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association, 219(1):51-56.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Hoffman, J.M., Creevy, K.E. and Promislow, D.E. (2013). Reproductive capability is associated with lifespan and cause of death in companion dogs. PloS one, 8(4), p.e61082.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Hoffman, M.D., Blei, D.M., Wang, C. and Paisley, J. (2013). Stochastic variational inference. Journal of Machine Learning Research.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Howe, L.M. (2006). Surgical methods of contraception and sterilization. Theriogenology, 66(3):500-509.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Jacob M. S, Philip A. B, Kimberly W. (2020). Mississippi State University College of Veterinary Medicine
Publisher | Google Scholor - Karadjole, T., Macesic, N., Beck, A., Folnožić, I., Prvanovic, et al. (2012). Laparoscopic ovariohysterectomy in a bitch with endometrial hyperplasia-a case report. Veterinarski arhiv, 82(3):311-318.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kristiansen VM, Nodtvedt A, Breen AM, Langeland M, Teige J, Goldschmidt M, Jonasdottir TJ, Grotmol T & Sørenmo K., (2013). Effect of ovariohysterectomy at the time of tumor removal in dogs with benign mammary tumors and hyperplastic lesions: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Journal Veterinary Intern Medicine, 27(4):935-942.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kuhne, F., (2012). Castration of dogs from the standpoint of behaviour therapy. Tierarztliche Praxis. Ausgabe K, Kleintiere/Heimtiere, 40(2):140-145.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kustritz, M.V.R., (2007). Determining the optimal age for gonadectomy of dogs and cats. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association, 231(11):1665-1675.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kutzler, M.A., (2020). Gonad-sparing surgical sterilization in dogs. Frontiers in Veterinary Science:342.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Lansdowne, J.L., Mehler, S.J. and Bouré, L.P., (2012). Minimally invasive abdominal and thoracic surgery: principles and instrumentation. Compend Contin Educ Vet, 34(5), E1.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Levy J. (2004).Feral cat management, in Miller L, Zawistowski S (eds): Shelter Medicine for Veterinarians and Staff.Ames, IA, Blackwell Publishing:381–385.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Lhermette, P., D. Sobel (2008): Rigid endoscopy: Laparoscopy. In: BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Endoscopy and Endosurgery. British Small Animal Veterinary Association. Gloucester:158-173.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Louis, R. (2012). Surgery of the spine: surgical anatomy and operative approaches. Springer Science & Business Media.
Publisher | Google Scholor - McGrath, H., Hardie, R.J. and Davis, E. (2004). Lateral flank approach for ovariohysterectomy in small animals. Compend Contin Educ Pract Vet, 26:922-930.
Publisher | Google Scholor - McKenzie, B., (2010). Evaluating the benefits and risks of neutering dogs and cats. CAB Rev, 5(45):1-18.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Munoz Rojas, M.A., Vargas Rodríguez, I.M. and Soler-Tovar, D., (2011). Métodos para el control de poblaciones caninas: una introducción. Una Salud. Revista Sapuvet de Salud Pública, 2(1):63-79.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Murphy, C.J., Samuelson, D.A., Pollock, R.V.H., Evans, H. and de Lahunta, A., (2012). Miller’s Anatomy of the Dog.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Murthy, V., Murthy, C., Jamuna, K. and Nagaraja, B. (2012). Comparison of different laparotomy techniques of ovariohysterectomy and post-surgical complications in dogs. Deptt. of veterinary gynecology & obstetrics, 4(2):116-118.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Murugesan, V., Arunachalam, K., Shanmugam, K. and Palanivel, M. (2020). Comparative study on midline and lateral flank approaches for ovariohysterectomy in cats. Pharma. Innov. J, 9:191-193.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Overley, B., Shofer, F.S., Goldschmidt, M.H., Sherer, D. and Sorenmo, K.U. (2005). Association between ovarihysterectomy and feline mammary carcinoma. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 19(4):560-563.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Raymond, T.N., Roland, M.E., Françoise, K.M., Francis, Z., Livo, et al. (2015). Do open garbage dumps play a role in canine rabies transmission in Biyem-Assi health district in Cameroon? Infection ecology & epidemiology, 5(1):26055.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Rebbeck, C.A., Thomas, R., Breen, M., Leroi, A.M. and Burt, A. (2009). Origins and evolution of a transmissible cancer. Evolution: International Journal of Organic Evolution, 63(9):2340-2349.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Reichler, I.M. (2009). Gonadectomy in cats and dogs: a review of risks and benefits. Reproduction in Domestic Animals, 44:29-35.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Robertson, S. (2008). Perspectives in Agriculture, Veterinary Science, Nutrition and Natural Resources, 3, 046:11.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Romagnoli, S. (2008). October. Surgical gonadectomy in the bitch and queen: should it be done and at what age. In Southern European Veterinary Conference and Congreso Nacional AVEPA.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Rosewell, L., (2016). Laparoscopic or traditional bitch spay? A comparison of surgical technique, associated risks and benefits. Veterinary Nursing Journal, 31(2):53-58.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Sallander, M., Hedhammar, Å., Rundgren, M. and Lindberg, J.E., (2001). Demographic data of a population of insured Swedish dogs measured in a questionnaire study. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica, 42(1):1-10.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Simpson, M., Albright, S., Wolfe, B., Searfoss, E., Street, et al. (2019). Age at gonadectomy and risk of overweight/obesity and orthopedic injury in a cohort of golden retrievers. PLoS One, 14(7):e0209131.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Slatter, D.H. ed., 2003. Textbook of small animal surgery (1). Elsevier health sciences.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Smith, K., (2015). Chew Deterrent Protective Dog Collar and Method. U.S. Patent Application 14/214,937.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Talukder, A.K., Das, Z.C., Rahman, M.A., Rahman, M.T. and Rahman, A.N., (2021). Caesarean section followed by ovariohysterectomy in a Bangladeshi domestic cat: A surgical intervention for management of dystocia due to partial primary uterine inertia. Veterinary Medicine and Science, 7(5):1564-1568.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Tivers, Mickey, and Stephen Baines.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Trevejo, R., Yang, M. and Lund, E.M., (2011). Epidemiology of surgical castration of dogs and cats in the United States. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association, 238(7):898-904.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Van Goethem, B., Schaefers‐Okkens, A.U.K.E. and Kirpensteijn, J., (2006). Making a rational choice between ovariectomy and ovariohysterectomy in the dog: a discussion of the benefits of either technique. Veterinary Surgery, 35(2):136-143.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Van Goethem, B., Schaefers‐Okkens, A.U.K.E. and Kirpensteijn, J., (2006). Making a rational choice between ovariectomy and ovariohysterectomy in the dog: a discussion of the benefits of either technique. Veterinary Surgery, 35(2):136-143.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Van Meervenne, S., Volk, H.A., Verhoeven, P.S., Van Ham, L. and O’Neill, D.G. (2019). Associations between neutering and idiopathic epilepsy in Labrador retrievers and border collies under primary veterinary care in the UK. The Veterinary Journal, 252:105354.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Waters, D.J., Kengeri, S.S., Maras, A.H. and Chiang, E.C., (2011). Probing the perils of dichotomous binning: how categorizing female dogs as spayed or intact can misinform our assumptions about the lifelong health consequences of ovariohysterectomy. Theriogenology, 76(8):1496-1500.
Publisher | Google Scholor - WHO (2004). Technical Report Series 931 World Health Organization Expert Consultation on Rabies in Geneva.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Wildt, D.E. and Lawler, D.F. (1985). Laparoscopic sterilization of the bitch and queen by uterine horn occlusion. American journal of veterinary research, 46(4):864-869.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Younis M.Faten F. Mohammed A. Abu-Seida M. Ragab R.S. and GoharH.M. (2014).Ultrasonography and Pathological Evaluation of Cystic Endometrial Hyperplasia Pyometra Complex in Bitches and Queens with Related Ovarian Alterations.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Zanowski, G.N., (2012). A fresh look at spay/neuter legislation: The journey to a middle ground. Journal of Public Health Management and Practice, 18(3):E24-E33.
Publisher | Google Scholor