Review Article
Role of Microbes in Biotechnology and Sustainable Agriculture
- Samra Ashfaq
- Nida Tabassum Khan *
Faculty of Life Sciences & Informatics, Department of Biotechnology, Balochistan University of Information Technology, Engineering and Management Sciences, Balochistan, Pakistan.
*Corresponding Author: Nida Tabassum Khan, Faculty of Life Sciences & Informatics, Department of Biotechnology, Balochistan University of Information Technology, Engineering and Management Sciences, Balochistan, Pakistan.
Citation: Ashfaq S., Khan N.T. (2024). Role of Microbes in Biotechnology and Sustainable Agriculture, International Journal of Biomedical and Clinical Research, BioRes Scientia Publishers. 2(1):1-10. DOI: 10.59657/2997-6103.brs.24.036
Copyright: © 2024 Nida Tabassum Khan, this is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Received: November 08, 2024 | Accepted: November 29, 2024 | Published: December 06, 2024
Abstract
Microbial biotechnology plays a crucial role in sustainable agriculture by harnessing beneficial microorganisms for various agricultural applications. This review explores the diverse roles of microbes in agriculture, focusing on their use as biofertilizers and biopesticides. Key microbial groups such as Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) and fungal biocontrol agents are highlighted for their contributions to enhancing crop nutrition, combating pests and diseases, and promoting environmental sustainability. The interaction dynamics within the plant microbiome, including the rhizosphere and endosphere, are also discussed, emphasizing their impact on plant health and productivity under changing climatic conditions.
Keywords: biotechnology; nutrition; PGPR; fungal biocontrol agents
Introduction
A rapidly expanding area of biological sciences called biotechnology has several uses in sustainable agriculture. In biological sciences, it entails employing genetic engineering to change living things or their components to produce useful products for various uses. The world's expanding population will significantly strain food production and agriculture by the end of 2033. In order to meet the rising demand for food, this offers a difficulty. A rapidly expanding area of biological sciences called biotechnology has several uses in sustainable agriculture. In biological sciences, it entails employing genetic engineering to change living things or their components to produce useful products for various uses. In order to meet the rising demand for food, this offers a difficulty. Experts like Mostafiz, Rahman & Rahman (2012) and Barea (2015) predict that by 2050, the demand for agricultural products will have increased by at least 70%. (Barea & nutrition, 2015; Rahman, Mostafiz, Paatero, Lahdelma, & Reviews, 2014) As more people become aware of the significance of food security, this understanding of the necessity for sustainable agriculture techniques will grow increasingly pronounced. Microbial biotechnology is essential for developing agricultural science in a number of areas, including nutrition, food security, and food safety. The basis for biotechnology research, technology development, and the production of new goods is genetic material derived from plants, animals, and microbes. By locating, isolating, cloning, and transferring desirable genes between species, biotechnology technologies have transformed breeding and rendered outdated the classic Mendelian population conceptions. Identifying genetic variants, comprehending how genes work, and improving transgenic organisms with particular advantageous features are the ultimate goals of biotechnology (R. Singh, Singh, Khush, & Rohilla, 2000). Globally, agricultural methods are used to achieve sustainable economic and environmental growth while protecting the environment. The junction of the economy and the environment (agroecology), environmental consciousness, and living standards are key components of the idea of "sustainable development." Developing effective strategies to reduce the negative consequences of environmental change, manage pests and illnesses, and recycle nutrients for sustainability, stressors are essential. For ecological and economic sustainability, controlling the microbiome of plant roots is crucial (Barea & nutrition, 2015). Agriculture biotechnology, general microbiology, and microbial ecology are all connected by agricultural microbiology. In both natural and agricultural ecosystems, it focuses on comprehending how microorganisms are distributed across plants, animals, and soil conditions (Habig, Hassen, & Swart, 2015). Recombinant DNA technology is used to artificially insert genes into the genetic makeup of transgenic plants. These genes may originate from unrelated creatures like bacteria or animals as well as from members of the same or other species (Ho, 2013). Various advantages of genetically modified crops include delayed ripening for longer shelf life, resistance to pests and diseases to use fewer pesticides, resistance to fungi and viruses, and tolerance to herbicides for better weed control (Hassoun et al., 2022; Phenica, Lakshmi, Prasad, & Ramu, 2018). By minimizing dependency on agrochemicals, notably pesticides, microbial biotechnology supports sustainable agriculture. It does this by introducing genes into attractive plant kinds that offer tolerance or resistance to biotic and abiotic stressors. Improved pest and disease resistance, increased resiliency to environmental pressures, bioremediation of dirty soils, higher production, and better nutrient uptake are only a few effects of biotechnology on sustainable agriculture. The employment of environmentally benign symbiotic microorganisms in place of hazardous fertilizers and pesticides is one promising method for sustainable agriculture. These bacteria have the ability to improve crop nutrition, defend against viruses and pests, and lessen the consequences of pollution and climate change. Natural resource management, environmental concerns, and public policy difficulties are just a few of the many facets that make up agriculture. It uses a variety of techniques (Lenzi, Marvasi, & Baldi, 2021).
Potential Significance of Beneficial Microbes in Sustainable Agriculture
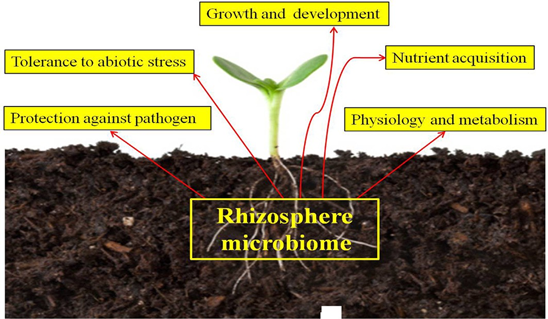
In the approaching decades, utilizing the advantageous microorganisms in sustainable crop production will become a key priority. The most biodiverse ecosystem on Earth is thought to exist in the soil matrix, which serves as a main repository for microorganisms that interact with plants. This environment's critical processes, which especially affect plant health, are controlled by the soil microbiome. The ability of the microbiome to give nutrients (phosphorus solubilization and nitrogen fixation), enhance nutrient uptake from the soil, and promote plant protection are just a few of the roles that have been attributed to it in tight relationships with plants (Gosal & Kaur, 2017). The natural soil microflora, which contains a variety of beneficial bacteria and fungi, including the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus known as plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR), is what organic farming depends on the most (Noumavo, Agbodjato, Baba-Moussa, Adjanohoun, & Baba-Moussa, 2016; Ramesh, Challenges, & Opportunities, 2019). The ability of beneficial microbes to digest phosphorus for their own needs—which is therefore available in sufficient amounts as its soluble form in soil—is one of their main advantages (Kafle et al., 2019). It has been documented that the solubilization process is actively carried out by the bacteria Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Micrococcus, Flavobacterium, Fusarium, Sclerotium, Aspergillus, and Penicillium (Kour et al., 2019). The main factors limiting the productivity of the crops are biotic and abiotic stressors (Yadav et al., 2020). For the purpose of improving crops under stress, many modern scientific technologies have been broadly linked, and the role of PGPRs as bioprotectants has emerged as being of particular significance in this regard (Odoh, 2017).
Figure 1: Rhizospheric soil.
Plant Microbe Interactions
Microorganisms, for example, can help and control nutrient availability and acquisition and promote stress tolerance, which can have an impact on agricultural output. The plant microbiome's species variety and microbial community richness, as well as the variables influencing it and its functioning, remain mostly unknown. The significance of this topic is Microbiome of the rhizosphere and sustainable agriculture. In recent years, there have been an increasing number of scholarly articles on this subject, as shown by studies concentrating on unique plant niches and how they modify their specific microbial populations. Understanding the key factors that influence the composition of the plant microbiome, which is a dynamic and adaptable part of the host, is crucial to changes in environmental (biotic and abiotic) conditions. Recent research has focused on different components of the plant microbiome independently in order to comprehend the variables that affect its assembly and the dynamics from a phylogenetic and functional perspective. The so-called rhizosphere, endosphere, and phyllo sphere are three significant compartments where microbial cells can establish and grow (Hirsch, Miller, & Dennis, 2013). Various significant crop species and their natural relatives have not yet been investigated for their associated bacterial communities, despite the fact that the plant microbiome is thought to be a vast treasure trove of microbial variety. Outbreaks have been documented to better comprehend the importance of the plant-associated microbiome in the protection of pathogens (Asraful Islam et al., 2010; Trif, Rusu, Francino, Delgado, & Rufián-Henares, 2022).
The development of a thorough understanding of the mechanisms underpinning plant-microbe interactions in the rhizosphere has been hampered by the absence of an adequate technique. The main difficulties stem from the requirement to profile an amazing group of processes where the diverse and large microbial communities are mostly made up of uncultivable microorganisms (Carvalhais, Dennis, Tyson, & Schenk, 2013). These molecular-based methodologies are crucial for determining how stresses caused by biotic and abiotic stress factors affect soil microbiome diversity and plant-microbe interactions in the context of current climate change. A greater knowledge of the interactions between plants and their microbiomes would enable soil bacteria to better relieve agricultural stress (Barea & nutrition, 2015). Numerous stressors, such as salt, drought, nutrient deficiency, pollution, diseases, and pests, among others, can change how plants and microbes interact in the rhizosphere (Velmourougane, Saxena, Prasanna, & Impacts, 2017). Researchers found that the structure of plant roots in soil can be affected by the presence of even little amounts of water. This discovery creates new opportunities for improving water and nutrient aging for significant food crops. The extent of root branching affects how effectively crops absorb water and absorb nutrients. Therefore, it is crucial to comprehend how root branching is regulated (Angers & Caron, 1998).
Microbial Interactions across Plant, Soil, and Environmental Interfaces
The majority of the other species that are connected to plants are bacteria. These include the rhizosphere, soil microorganisms connected to subterranean plants, endophytes within plants, and epiphytes on plant surfaces. organs and soil interfaces for sustainable agriculture using biotechnology. Agriculture places a special emphasis on the symbiosis between legume plants and soil-dwelling rhizobia, and more study has focused on characterizing the molecular processes that produce species-specific cooperation (Pinto et al., 2014). Host-specific flavonoids that are secreted in the root exudates influence interactions between legumes and rhizobia. Numerous rhizosphere bacteria have the ability to activate plant defense mechanisms by triggering a systemic response in plants. Induced systemic resistance, or ISR, is the term used to describe signaling pathways that result in increased host pathogen resistance after exposure to nonpathogenic root zone microorganisms (Van Loon, Bakker, & Pieterse, 1998; Yu et al., 2022).
ISR has been demonstrated to be induced by a number of bacteria, including Bacillus species, which have been utilized to examine advantageous effects under abiotic stress settings. Bacterial endophytes, which are used to improve plant agronomic characteristics and biologically control a variety of plant diseases, may be of particular interest because they have the benefit of being relatively protected from the competitive soil environment. In addition, they frequently grow in the same plant tissue where bacterial plant pathogens are discovered.
Types of Root-Associated Microorganisms
The saprophytic or symbiotic relationships between the plant and the prokaryotic bacteria and eukaryotic fungi have the potential to be harmful or advantageous depending on their trophic/living behaviors. A small subset of these microorganisms, referred to as "endophytes," is able to penetrate and reside within plant tissues, while the great majority of them remain in the rhizospheric soil or rhizoplane (Ruano-Rosa, Mercado-Blanco, & management, 2015). It is acknowledged that soil bacteria are an important part of the many interrelated elements that contribute to the environmental quality needed for a sustained, healthy food supply. The rhizodeposition pools are what draw microbes to and keep them in rhizosphere microhabitats (Hirsch et al., 2013). There are many different types of organisms in the soil microbiome, but studies on the soil microbiome have focused primarily on bacteria, fungus, and archaea.
Beneficial Rhizosphere Microorganisms
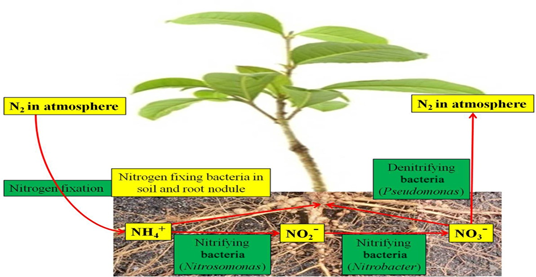
PGPR, antagonists of plant diseases, or decomposers of organic matter (detritus), beneficial saprophytic rhizosphere bacteria improve plant performance (Vessey & soil, 2003). The biological control of plant diseases and nitrogen cycling are just a couple of the important ecosystem processes that the PGPR are known to take part in (B. R. J. S. Glick, 2012). N2-fixing bacteria and multipurpose arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi are examples of beneficial plant mutualistic symbionts (Smith & Read, 2010). Rhizobia, a collective word for bacteria from several genera, are able to fix N2 in mutualistic symbiosis with legume plants (Peoples, Herridge, & Ladha, 1995). Nitrogen-fixing microorganisms turn atmospheric nitrogen to ammonia, which is then changed into forms that plants may use (ammonia and nitrate) (Dobbelaere, Vanderleyden, & Okon, 2003) (Fig. 6.2). A vast group of frequently unidentified or ill-defined microorganisms that interact well with plants and in soils are known as agriculturally relevant microfloras(Gray, Smith, & biochemistry, 2005).
Figure 2: Nitrogen-fixing microorganisms.
Plant-Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria
The transformation, mobilization, solubilization, and other processes that take place with regard to nutrients from a finite nutrient pool and, consequently, the uptake of crucial nutrients by plants to realize their full genetic potential (B. R. J. C. j. o. m. Glick, 1995). The use of PGPR has been identified as having a possible function in creating sustainable frameworks for crop production (Vessey & soil, 2003). The PGPR are distinguished by some inherent uniqueness, such as the ability to colonize the surface of the root or superficial intercellular spaces of the host plant; they must promote plant growth; they must survive, multiply, and compete with native microbiota in rhizosphere microhabitats at least for the time needed to express their beneficial plant growth promotion activities; and they must promote plant growth (Bashan & Holguin, 1998). Additionally, PGPR contributes to the solubilization of other nutrients and mineral phosphates, increases stress tolerance, and enhances soil structure and organic matter content (Rodrı́guez & Fraga, 1999). More soil-organic nitrogen is fixed by rhizospheric microorganisms in PGPR (Hayat, Ali, Amara, Khalid, & Ahmed, 2010). Therefore, they help in reducing the need for nitrogen and phosphate fertilizer and promote release of the nutrients. 192 Biotechnology for Sustainable Agriculture nitrogen, and other nutrients in the plant soil system (Richardson, Barea, McNeill, & Prigent-Combaret, 2009).
Function of PGPR
- Protection of the environment and natural resources (Adesemoye, Kloepper, & biotechnology, 2009)
- The solubilization of phosphorus (Rodrı́guez & Fraga, 1999)
- Manufacturing of growth regulators for plants (B. R. J. S. Glick, 2012)
- Mobilization of potash (Han & Lee, 2005)
- Microbes as biopesticides and fertilizers (Kloepper, Ryu, & Zhang, 2004)
- Manufacturing of volatile organic compounds (Ryu et al., 2003)
- Microorganisms as biotic triggers (Pieterse et al., 2014)
- Microbiological reactions to stress in agriculture (Yang, Kloepper, & Ryu, 2009)
- Microbiological conflict (Beneduzi, Ambrosini, Passaglia, & biology, 2012)
Mechanism of Action of PGPR in Rhizosphere Region
The entire microbial community in the rhizosphere niche is altered by PGPR-mediated plant growth promotion through the synthesis of different chemicals (B. R. J. S. Glick, 2012). Indirectly, PGPR increase plant growth by reducing the negative effects of various pathogens on plant growth and development in the form of biocontrol agents (Kloepper et al., 2004). Directly, PGPR encourage resource acquisition (nitrogen, phosphorus, and essential minerals) or balance plant hormone levels. Associative nitrogen fixation and PGPR's method of action are two common ways that microbes control plant nutrients (Richardson et al., 2009). lowering of ethylene levels, synthesis of siderophores, generation of growth regulators, VOCs, solubilization of nutrients, and encouragement of mycorrhizal activity (Lugtenberg & Kamilova, 2009). Microbial Biotechnology and Sustainable Agriculture. To fully implement bacterium-assisted phytoremediation of trace element-contaminated soils, key processes in plant bacteria interactions and colonization by inoculation strains still need to be elucidated (B. R. J. S. Glick, 2012).
Application of High-Quality Microbial Inoculants
A thorough analysis of the formulation and practical views of inoculants technology for PGPR was recently published by Bashan, de-Bashan, Prabhu, and Hernandez (2014). They suggest several major research goals for developing delivery methods for PGPR and rhizobia. The following requirements must be met for the successful application of microbial inoculants in agriculture: (1) strengthen the scientific and technological foundations of inoculum production and application; (2) develop specific normative for each type of inoculant and its application, whether to seeds, soil, or a transplanted plant that has already been microbeized; (3) establish quality-control protocols; (4) reduce the fluctuation of field results; and (5) spread knowledge by outlining benefits and drawbacks for society(Bashan, de-Bashan, Prabhu, Hernandez, & soil, 2014).
Seed Treatments for Sustainable Agriculture
Agricultural Seed Treatments for Sustainability 90% of food crops are grown from seed, making seed an essential component of sustainable growth in agricultural production. If not promptly dealt with, seed-borne, early-season illnesses and insects have devastating effects (Cook, 2000). In modern agriculture, the focus is on producing more with less land, water, and labor. In order to combat plant pathogens, traditional environmentally friendly disease management techniques like sanitation, crop rotation, mixed cropping, adjusting the date of sowing, fallowing, summer plowing, green manuring composting, etc. are currently being reevaluated as a part of integrated pest management (Cook, 2000).
Encourage Beneficial Microbe Establishment at Rhizosphere
Gaining a biased rhizosphere undoubtedly creates new prospects for agricultural advancements based on utilizing advantageous microbial services to reduce pesticide inputs and so achieve sustainable environmental and economic goals (Philippot, Raaijmakers, Lemanceau, & Van Der Putten, 2013).
- Using agricultural practices to harness the microbial communities in the rhizosphere.
- Understanding how plants influence the rhizosphere's microbial community structure (Philippot et al., 2013).
- The idea or practice of the "biased rhizosphere".
In order to ascertain whether the rhizosphere may be manipulated (biased) to strengthen beneficial organisms while preventing the presence of diseases, a number of approaches are currently being pursued. Due to the considerable gaps in our understanding, the objective research themes present numerous challenges (Philippot et al., 2013).
Beneficial Microbes in Agriculture under Changing-Climatic Scenario
One of the main issues facing the world today is climate change, which has an impact on life on Earth. The general shape, functioning, and photosynthesis (the assimilation of carbon) of plant specimens as well as their interactions are typically impacted by climate change (Lobell & Gourdji, 2012). A rise in atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) lowers the nitrogen content of crops, which may delay the onset of many pests and illnesses and alter the makeup of the weed flora that grows alongside the crops (Taub & Wang, 2008). Agriculture suffers a variety of difficulties as a result of the excessive and illegal usage of chemical fertilizers (Bhattacharyya, Sarmah, Dutta, & Tanti, 2015). It is well recognized that a significant portion of the vital, naturally occurring micro- and macronutrients in soil are destroyed by synthetic fertilizers (Bhattacharyya et al., 2015). Changes in plant physiology and root exudation are anticipated to result from changes in environmental conditions brought on by a changing climate. To advance our understanding of native biodiversity and microbial community structure in the context of a changing climate, research is crucial (B. K. Singh, Bardgett, Smith, & Reay, 2010).
Biofertilizers
A preparation containing active or dormant cells of effective strains of nitrogen-fixing, phosphate-solubilizing, and cellulytic microorganisms, among others, is referred to as a biofertilizer (Vessey & soil, 2003). Biofertilizers, in contrast to chemical fertilizers, are living microorganisms that aid plants in accessing the nutrient availability in the rhizosphere but do not themselves produce nutrients (Bhardwaj, Ansari, Sahoo, & Tuteja, 2014). Numerous microorganisms, such as nitrogen-fixing soil bacteria (Azotobacter, Rhizobium), nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria (Anabaena), phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (Pseudomonas sp.), and AM fungus, are frequently utilized as biofertilizers (Bashan & De-Bashan, 2010). Similar to this, cellulolytic microorganisms and phytohormone (auxin)-producing bacteria are also utilized in the creation of biofertilizers (Rodrı́guez & Fraga, 1999). These microbial formulations are used to speed up specific microbial processes so that more nutrients are available in plant-assimilable forms (Richardson et al., 2009). A cheap and sustainable source of plant nutrients is biofertilizers. These are the types of helpful soil microorganisms that have been cultivated and packaged in the lab in acceptable carriers. A material that gives a biofertilizer formulation a longer shelf life is known as a carrier. Examples include peat, lignite powder, vermiculite, clay, talc, rice bran, seed, charcoal, soil, rock phosphate pellets, paddy straw compost, wheat bran, and combinations of these materials (Bashan et al., 2014).
Biopesticides
(Table 1). Using biotechnology to create synthetic insecticide alternatives to combat insect pests is also acceptable (Bailey, Boyetchko, & Längle, 2010). To safeguard the plant throughout the crucial seedling stage, coating formulas for these helpful organisms may be created. Bacterial and fungal agents like Trichoderma spp., Ampelomyces quisqualis (used to combat grape powdery mildew), and Bacillus subtilis (used to control plant diseases) are frequently utilized as second-hand biopesticides (Glare et al., 2012). A microorganism with the agile attribute either directly affects the pathogen as a biocontrol agent (such as Contans) or creates a chemical during fermentation that functions as a control (such as Sonata) (Fravel, 2005).
Table 1: Categories of Microbial Biopesticides.
| Category | Microorganisms | Target Pest | Mode of Action | Reference |
| Bactericide | Agrobacterium Radiobacter | Crown Gall (Agrobacterium Tumefaciens) | Antagonist and Antibiosis | Ochsner et al., 2013 |
| Bacillus Polymyxa | Crown Gall | Antagonist and Antibiosis | Chen et al., 2007 | |
| Bacillus Sphaericus | Crown Gall | Antagonist and Antibiosis | Palma-Guerrero et al., 2010 | |
| Bacillus Subtilis | Bacterial Pathogen | Colonizes on Plant Root and Competes | Borriss, 2011 | |
| Pseudomonas Fluorescens | Several Bacterial Diseases Such as Frost-Forming Bacteria | Crowds Out and Controls the Growthof Plant Pathogens | Haas And Defago, 2005 | |
| Fungicide | Bacillus Subtilis | Soil Foliage, Fungal Pathogens Such as Rhizoctonia, Fusarium, Aspergillus, and Others | Colonizes on Plant Root and Competes and Antibiosis | Compant et al., 2005 |
| Pseudomonas Syringae | Postharvest Disease | Utilize Seed Exudates, Produce A Wide Spectrum of Bioactive Metabolites | Schnider-Keel et al., 2000 | |
| Bacillus Pumilus | Seedling Disease | Colonizes on Plant Rootand Competes and Antibiosis | Mukherjee et al., 2012 | |
| Streptomyces | Fungi-Causing Damping Off, Stem, And Crown Rots | Mycoparasitic, Antagonist, and Antibiosis | Harman et al., 2004 | |
| Pseudomonas Fluorescens | Plant Soil-Borne Diseases, Fireblight | Utilize Seed and Root Exudates and Colonize, Produce A Wide Spectrum of Bioactive Metabolites | Lugtenberg and Kamilova, 2009 | |
| Trichoderma Viride/ Harzianum | Soil-Borne Fungal Disease | Mycoparasitic, Antagonist, and Antibiosis | Lorito et al., 2010 | |
| Burkholderia Cepacia | Fungal Pathogens | Controls Fungi Via Seed Treatment | Coenye and Vandamme, 2003 | |
| Gliocladium Catenulatum | Seed-Borne and Soil- Borne Diseases | Enzymatic Mechanism | Gams et al., 1998 | |
| Candida Oleophila | Postharvest Pathogens | Colonization of Diseased Tissues | Mercier and Jiménez, 2004 |
The argument for consistent home cooking has made conventional agriculture heavily reliant on pesticides. Growers are investigating new ecologically friendly methods to replace, or at least augment, the current chemical-based processes as a result of the growing clientele and spend on shipboard maintenance. Biopesticides have gained popularity as a potential replacement for chemical pesticides. The efficacy of biopesticide bacteria such as Bacillus circulans, Agrobacterium radiobacter, Bacillus pumilus, and Pseudomonas aureofaciens and fungi such as Ampelomyces quisqualis, Fusarium oxysporum, Gliocladium virens, Trichoderma harzianum, and Pythium oligandrum was utilized by many countries for their growth in the field of agriculture for sustainable development (Hynes & Boyetchko, 2006).
Conclusion
Biotechnology is becoming increasingly important in the constantly expanding field of sustainable agriculture. This discipline uses genetic resources from plants, animals, and microbes to create novel solutions for sustaining agricultural output while protecting the environment. Sustainable agriculture methods include a variety of techniques and tactics that address economic and environmental problems while taking into account the complex interplay of social, physical, and biological aspects. Agriculture has an impact that extends beyond agricultural cultivation to include the management of critical natural resources such as surface and groundwater, forests, recreational areas, and wildlife. Climate change is a major global issue that affects all life on Earth, and sustainable agriculture aims to limit its consequences. Biodiversity, the foundation of all agricultural plants and animals, is crucial to agricultural success. Agro ecology, which uses natural biodiversity to increase crop productivity, is a popular technique. This is accomplished by cultivating beginning crops, which improves the environmental conditions for later crops. In essence, sustainable agriculture attempts to integrate agricultural practices with ecological and economic sustainability, addressing pressing global concerns while guaranteeing the well-being of both people and the environment. It is driven by biotechnology and a thorough understanding of genetic resources.
References
- Adesemoye AO, Kloepper JW. (2009). Plant-Microbes’ Interactions in Enhanced Fertilizer-Use Efficiency. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 85(1):1-12.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Denis A., Jean C. (1998). Plant-Induced Changes in Soil Structure: Processes and Feedbacks. Biogeochemistry. 42:55-72.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Asraful Islam SM, Math RK, Kim JM, Yun MG, Cho JJ, et al. (2010). Effect of Plant Age on Endophytic Bacterial Diversity of Balloon Flower (Platycodon Grandiflorum) Root and Their Antimicrobial Activities. Curr Microbiol. 61(4):346-356.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Bailey K.L., Susan B., Tobias L. (2010). Social and Economic Drivers Shaping the Future of Biological Control: A Canadian Perspective on The Factors Affecting the Development and Use of Microbial Biopesticides. Biological Control. 52:221-229.
Publisher | Google Scholor - J. M. Barea. (2015). Future Challenges and Perspectives for Applying Microbial Biotechnology in Sustainable Agriculture Based on A Better Understanding of Plant-Microbiome Interactions, Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition. 15(2):261-282.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Bashan, Yoav & de-Bashan, Luz & Prabhu, SR & Hernandez, Juan. (2014). Advances In Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterial Inoculant Technology: Formulations and Practical Perspectives (1998-2013). Plant and Soil. 378:1-33.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Bashan Y., De-Bashan L. (2010). How The Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Azospirillum Promotes Plant Growth-A Critical Assessment. Advances in Agronomy. 108:77-136.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Bashan, Y., Holguin, G. (1998). Proposal For the Division of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria into Two Classifications: Biocontrol-PGPB (Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria) and PGPB. Soil Biol Biochem. 30(8-9):1225-1228.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Beneduzi A., Ambrosini A., Passaglia L. (2012). Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR): Their Potential as Antagonists and Biocontrol Agents. Genet Mol Biol. 35(4):1044-1051.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Bhardwaj, D., Ansari, M. W., Sahoo, R. K., Tuteja, N. (2014). Biofertilizers Function as Key Player in Sustainable Agriculture by Improving Soil Fertility, Plant Tolerance and Crop Productivity. Microb Cell Fact. 13:66.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Bhattacharyya P., Sarmah S., Dutta P., Tanti A. (2015). Emergence In Mapping Microbial Diversity in Tea (Camellia Sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) Soil of Assam, North-East India: A Novel Approach. European Journal of Biotechnology and Bioscience. 3(12):20-25.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Borriss R. (2011). Use Of Plant-Associated Bacillus Strains as Biofertilizers and Biocontrol Agents in Agriculture. Bacteria in Agrobiology: Plant Growth Responses. 41-76.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Compant S, Duffy B, Nowak J, Clément C, Barka EA. (2005). Use of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria for Biocontrol of Plant Diseases: Principles, Mechanisms of Action, and Future Prospects. Appl Environ Microbiol. 71(9):4951-4959.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Coenye T., Vandamme P. (2003). Diversity and Significance of Burkholderia Species Occupying Diverse Ecological Niches. Environmental Microbiology, 5(9):719-729.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Carvalhais LC., Dennis PG., Tyson GW., Schenk P. (2013). Rhizosphere Meta Transcriptomics: Challenges and Opportunities. In Molecular Microbial Ecology of the Rhizosphere. 1:1137-1144.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Cook RJ. (2000). Advances in Plant Health Management in the Twentieth Century. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 38:95-116.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Dobbelaere S., Vanderleyden J., Okon Y. (2003). Plant Growth-Promoting Effects of Diazotrophs in the Rhizosphere. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences. 22(2):107-149.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Fravel DR. (2005). Commercialization and Implementation of Biocontrol. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 43:337-359.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Glare T, Caradus J, Gelernter W, Jackson T, Keyhani N, et al. (2012). Have Biopesticides Come of Age? Trends Biotechnol. 30(5):250-258.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Glick B. (1995). The Enhancement of Plant Growth by Free-Living Bacteria. Canadian Journal of Microbiology. 41(2):109-117.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Glick B. (2012). Plant Growth‐Promoting Bacteria: Mechanisms and Applications. Scientifica (Cairo). 963401.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Gosal SK, Kaur J. (2017). Microbial Inoculants: A Novel Approach for Better Plant Microbiome Interactions. Probiotics in Agroecosystem. 269-289.
Publisher | Google Scholor - E.J. Gray, D.L. Smith. (2005). Intracellular and extracellular PGPR: commonalities and distinctions in the plant–bacterium signaling processes, Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 37(3):395-412.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Gams, W., Hoekstra, E. S., Aptroot, A. (1998). CBS Course of Mycology (4th Edn). Mycopathologia, 143(1):53-97.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Habig, Johan & Hassen, Ahmed & Swart, Antoinette. (2015). Application of Microbiology in Conservation Agriculture. Conservation Agriculture. 525-557.
Publisher | Google Scholor - H.S. Han, K.D. Lee. (2005). Phosphate and Potassium Solubilizing Bacteria Effect on Mineral Uptake, Soil Availability and Growth of Eggplant, Research Journal of Agriculture and Biological Sciences, 1(2):176-180.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Hassoun A, Cropotova J, Trif M, Rusu AV, Bobis O, et al. (2022). Consumer Acceptance of New Food Trends Resulting from The Fourth Industrial Revolution Technologies: A Narrative Review of Literature and Future Perspectives. Front Nutr. 9:972154.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Hayat, R., Ali, S., Amara, U. et al. (2010). Soil Beneficial Bacteria and Their Role in Plant Growth Promotion: A Review. Ann Microbiol. 60:579-598.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Hirsch, P.R., Miller, A.J., Dennis, P.G. (2013). Do Root Exudates Exert More Influence on Rhizosphere Bacterial Community Structure Than Other Rhizodeposits? In Molecular Microbial Ecology of the Rhizosphere.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Mae-Wan Ho. (2013). The New Genetics and Natural Versus Artificial Genetic Modification. Entropy, 15(11):4748-4781.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Harman GE, Howell CR, Viterbo A, Chet I, Lorito M. (2004). Trichoderma Species--Opportunistic, Avirulent Plant Symbionts. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2(1):43-56.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Hynes, Russell & Boyetchko, Susan. (2006). Research Initiatives in The Art and Science of Biopesticide Formulations. Soil Biology and Biochemistry. 38:845-849.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Haas D, Défago G. (2005). Biological Control of Soil-Borne Pathogens by Fluorescent Pseudomonads. Nat Rev Microbiol. 3(4):307-319.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kafle A., Cope K.R., Raths R., Yakha J.K., Subramanian S., et al. (2019). Harnessing Soil Microbes to Improve Plant Phosphate Efficiency in Cropping Systems, Agronomy, 9(3):127.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kloepper JW, Ryu CM, Zhang S. (2004). Induced Systemic Resistance and Promotion of Plant Growth by Bacillus spp. Phytopathology. 94(11):1259-1266.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kour D., Rana K.L., Yadav A.N., Yadav N., Kumar V., et al. (2019). Drought-Tolerant Phosphorus-Solubilizing Microbes: Biodiversity and Biotechnological Applications for Alleviation of Drought Stress in Plants. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria for Sustainable Stress Management, 255–308.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Anna Lenzi, Massimiliano Marvasi, Ada Baldi. (2021). Agronomic Practices to Limit Pre- and Post-Harvest Contamination and Proliferation of Human Pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae in Vegetable Produce. Food Control. 119:107486.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Lobell DB, Gourdji SM. (2021). The Influence of Climate Change on Global Crop Productivity. Plant Physiol. 160(4):1686-1697.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Lugtenberg B, Kamilova F. (2009). Plant-Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 63:541-556.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Lorito M, Woo SL, Harman GE, Monte E. (2010). Translational Research on Trichoderma: From 'Omics to The Field. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 48:395-417.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Mukherjee, P. K., Horwitz, B. A., Singh, U. S. (2012). Trichoderma: Biology and Applications. Current Science, 102(5):721-728.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Angela Corcelli, Veronica M. T. Lattanzio, Giuseppe Mascolo, Francesco Babudri, Aharon Oren, et al. (2004). Novel Sulfonolipid in The Extremely Halophilic Bacterium Salinibacter Ruber. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70(11):6677-6685.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Noumavo, Agossou D. P. & Agbodjato, Nadège & Baba-Moussa, Farid & Adjanohoun, Adolphe & Baba-Moussa, Lamine. (2016). Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria: Beneficial Effects for Healthy and Sustainable Agriculture. African Journal of Biotechnology. 15(27):1452-1463.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Odoh, Chuks. (2017). Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR): A Bioprotectant bioinoculant for Sustainable Agrobiology: A Review. International Journal of Advanced Research in Biological Sciences, 4:123-142.
Publisher | Google Scholor - M. B. Peoples, D. F. Herridge, J. K. Ladha. (1995). Biological Nitrogen Fixation: An Efficient Source of Nitrogen for Sustainable Agricultural Production? Management of Biological Nitrogen Fixation for the Development of More Productive and Sustainable Agricultural Systems. 3-28.
Publisher | Google Scholor - B. Affia Phenica, T. Lakshmi, S.V. Prasad, Y. Reddi Ramu. (2018). A Study on Production Constraints of Rice Cultivation in Kurnool District of Andhra Pradesh and Suggestions to Overcome Them. International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences. 7(11):2364-2368.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Philippot L, Raaijmakers JM, Lemanceau P, Van der Putten WH. (2013). Going Back to The Roots: The Microbial Ecology of The Rhizosphere. Nat Rev Microbiol. 11(11):789-799.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Pieterse CM, Zamioudis C, Berendsen RL, Weller DM, Van Wees SC, et al. (2014). Induced Systemic Resistance by Beneficial Microbes. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 52:347-375.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Pinto C, Pinho D, Sousa S, Pinheiro M, Egas C, et al. (2014). Unravelling The Diversity of Grapevine Microbiome. PLoS One. 9(1):e85622.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Md. Mizanur Rahman, Suraiya B. Mostafiz, Jukka V. Paatero, Risto Lahdelma. (2014). Extension of Energy Crops on Surplus Agricultural Lands: A Potentially Viable Option in Developing Countries While Fossil Fuel Reserves Are Diminishing. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 29:108-119.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Vivek Kumar, Ram Prasad, Manoj Kumar, Devendra K. Choudhary. (2019). Microbiome in Plant Health and Disease Challenges and Opportunities: Challenges and Opportunities. Springer. 191-213.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Richardson AE, Barea JM, McNeill AM, Prigent-Combaret C. (2009). Acquisition of Phosphorus and Nitrogen in The Rhizosphere and Plant Growth Promotion by Microorganisms. Plant Soil. 321:305-339.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Rodríguez H, Fraga R. (1999). Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria and Their Role in Plant Growth Promotion. Biotechnol Adv. 17(4-5):319-339.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Ruano-Rosa, David & Mercado-Blanco, Jesús. (2015). Combining Biocontrol Agents and Organics Amendments to Manage Soil-Borne Phytopathogens. Organic Amendments and Soil Suppressiveness in Plant Disease Management. 457-478.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Ryu CM, Farag MA, Hu CH, Reddy MS, Wei HX, et al. (2003). Bacterial volatiles promote growth in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 100(8):4927-4932.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Singh BK, Bardgett RD, Smith P, Reay DS. (2010). Microorganisms and climate change: terrestrial feedbacks and mitigation options. Nat Rev Microbiol. 8(11):779-790.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Singh, R., Singh, U., Khush, G., Rohilla, R. (2000). Genetics and Biotechnology of Quality Traits in Aromatic Rices. Aromatic Rices. 5:47-70.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Sally E. Smith, David Read. (2008). Mycorrhizal Symbiosis.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Schnider-Keel U, Seematter A, Maurhofer M, Blumer C, Duffy B, et al. (2000). Autoinduction Of 2,4-Diacetylphloroglucinol Biosynthesis in The Biocontrol Agent Pseudomonas Fluorescens CHA0 And Repression by The Bacterial Metabolite’s Salicylate and Pyoluteorin. J Bacteriol. 182(5):1215-1225.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Taub DR, Wang X. (2008). Why Are Nitrogen Concentrations in Plant Tissues Lower Under Elevated CO2? A Critical Examination of The Hypotheses. J Integr Plant Biol. 50(11):1365-1374.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Monica Trif, Alexandru Vasile Rusu, M. Pilar Francino, Gabriel Delgado, Jose Ángel Rufián-Henares. (2022). Microbiome Applications for Sustainable Food Systems. Biodiversity, Functional Ecosystems and Sustainable Food Production. 243-273.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Van Loon LC, Bakker PA, Pieterse CM. (1998). Systemic Resistance Induced by Rhizosphere Bacteria. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 36:453-483.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kulandaivelu Velmourougane, Garima Saxena, Radha Prasanna. (2017). Plant-Microbe Interactions in the Rhizosphere: Mechanisms and Their Ecological Benefits. Plant-Microbe Interactions in Agro-Ecological Perspectives. 193-219.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Vessey, Joseph. (2003). Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria as Biofertilizer. Plant and Soil. 255:571-586.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Yadav, S., Modi, P., Dave, A., Vijapura, A., Patel, D., et al. (2020). Effect of Abiotic Stress on Crops. IntechOpen. 3(17):5-16.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Yang J, Kloepper JW, Ryu CM. (2009). Rhizosphere Bacteria Help Plants Tolerate Abiotic Stress. Trends Plant Sci. 14(1):1-4.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Yu Y, Gui Y, Li Z, Jiang C, Guo J, et al. (2022). Induced Systemic Resistance for Improving Plant Immunity by Beneficial Microbes. Plants (Basel). 11(3):386.
Publisher | Google Scholor