Short report
Improvement of Graphene Induced Transverse Myelitis, with Preventing to Progress Spinal Shock by Graphene Exfoliator Nacl with Kcl Solution
Department of Emergency Medicine, New life Hospital Bokhyun-dong, Bukgus, Daegu, Korea.
*Corresponding Author: Chur Chin,Department of Emergency Medicine, New life Hospital Bokhyun-dong, Bukgus, Daegu, Korea.
Citation: Chin C. (2024). Improvement of graphene induced transverse myelitis, with preventing to progress spinal shock by graphene exfoliator NaCl with KCl solution, International Journal of Medical Case Reports and Reviews, BioRes Scientia Publishers. 3(3):1-2. DOI: 10.59657/2837-8172.brs.24.051
Copyright: © 2024 Chur Chin, this is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Received: March 20, 2024 | Accepted: April 10, 2024 | Published: April 13, 2024
Abstract
An 81-year-old man who had anterior cervical discectomy and fusion due to C4-5 cervical myelopathy 2 weeks ago, presented to our hospital with severe back pain and quadriparesis. The patient has a past medical history of tuberculosis (TB) infection.
Keywords: blood ;heart; systolic; diastolic
Introduction: Case Description
vital signs: blood pressure 90 (systolic) / 50 (diastolic), heart rate 64, total leukocyte count of 112100/cmm, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) 50 mm in the first hour using Westergren method, C-reactive protein (CRP) 0.84 mg/dl, thrombin time (PT) 16.9 second, prothrombin time (PTT) 27.2 second, international normalized ratio (INR) 1.66 and alkaline phosphatase 411 U/L. The intravenous infusion of a solution consisting of 250 mL normal saline with potassium chloride (KCl) over 6 h, vitamin C intake resulted in recovery of back pain symptom with normalized blood pressure (150/60) [1-7]. Transverse myelitis is a rare neurological condition that may originate from an inflammation-driven mechanism. Diagnosis is driven by confirming that symptoms originate from the spinal cord. After excluding structural causes, imaging will lead to visualization of abnormal cord signal. In most cases, this condition responds well to proper treatment. However, transverse myelitis can cause rapid loss of function, especially if not recognized and managed immediately. Imaging evidenced no significant structural defects but did lead to discovery of cord enhancement compatible with a diagnosis of transverse myelitis. Corticosteroid treatment was initiated rapidly to address this pathology, and the patient recovered without deficits. Previous tuberculosis infection could be a less likely cause of the neurological symptoms [8].
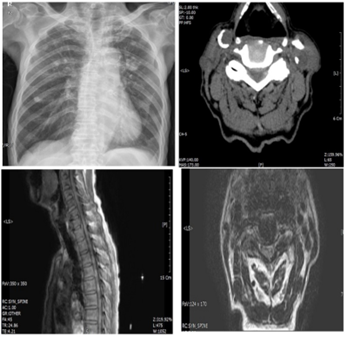
Figure 1: Baseline chest X-ray showing a cavity in the left lung and multiple foci in the upper lobes of both lungs. . Preoperative Computed Tomgram (CT) and T1-weighted sagittal (A) and axial (B) magnetic resonance images revealing a large C4-C5 disc herniation, compressing the right side of the spinal cord.
References
- Chin C. (2023). Comparison of 50 Cases of the Anti-Cancer Effects of NaCl with KCl as a Potent Graphene Exfoliator, Prehydrated Patients to NaCl-Only Prehydrated Patients on the Terminal Stage Cancer Patients. Case Reports in Clinical Medicine, 12:425-431.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Chin C. (2023). Changes in electrocardiogram after intramuscular injection of graphene using salt- intercalation exfoliation. J Clin Exp Cardiol, 14:1-15.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Chin C. (2021). Cell entry inhibitor with sulfonated colloid gold as new potent broad spectrum virucides. J Infect Dis Ther, 9:1-4.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Chin C. (2023). The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of NaCl with KCl as a Potent Graphene Exfoliator in a Patient with Guillaine-Barré Syndrome and Facial Nerve Palsy. Case Reports in Clinical Medicine, 12:447-451.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Chin C. (2023). Improvement of renal functions, graphene-induced rapid progression of prediabetes in an elderly woman with arthritis by graphene-exfoliator NaCl with KCl solution, 3 cases. Journal of Clinical Images and Medical Case Reports, 4:1-3.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Chin C. (2023). Improvement of graphene induced pulmonary edema by graphene exfoliator NaCl with KCl solution, Journal of Clinical Images and Medical Case Reports, 4:4-5.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Chin C. (2023). The anti-inflammatory effects of NaCl with KCl as a potent graphene exfoliator in a patient with interstitial pneumonia by epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Journal of Clinical Images and Medical Case Reports. 4:36-37.
Publisher | Google Scholor - So Hyun Ahn, Jae-Seok Kim, Jong Seok Bae, Yerim Kim. (2018). Multifocal Longitudinally Extensive Transverse Myelitis as a Rare Complication of Mumps Infection, J Neurosonol Neuroimag, 10(1): 37-40.
Publisher | Google Scholor