Research Article
Frequency, Types, and Factors Leading to Medication Error Among ICU Technologist, Respiratory Therapist and Nurses, at Tertiary Care Hospital Peshawar, Pakistan
- Sadiq Ullah *
Department of Respiratory Therapy, Khyber Medical University, Peshawar, Pakistan.
*Corresponding Author: Sadiq Ullah, Department of Respiratory Therapy, Khyber Medical University, Peshawar, Pakistan.
Citation: Ullah S. (2024). Frequency, Types, and Factors Leading to Medication Error Among ICU Technologist, Respiratory Therapist and Nurses, at Tertiary Care Hospital Peshawar, Pakistan, International Journal of Biomedical and Clinical Research, BioRes Scientia Publishers. 1(2):1-7. DOI: 10.59657/2997-6103.brs.24.008
Copyright: © 2024 Sadiq Ullah, this is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Received: April 15, 2024 | Accepted: June 03, 2024 | Published: June 11, 2024
Abstract
A proper contribution to understand the aspect that spread errors of medication is the basic step toward preventing them. There are countless types of medicine errors such as low or high dose, unsuitable site of administered drugs and time of dosage which occurs due to lack of pharmacological knowledge. Survey from United State in 2007 shows that 97% of doctors and nurses are worried about errors of medication. The major result of wrong medicine administered has increase the patient morbidity and mortality rate. In the various studies worldwide, the errors of medication and it factors increase day by day, the frequency of medication errors increases with various factors such as lookalike medicine, sound alike medicine, medicine use in rare cases and using acronyms drugs name. This is a descriptive cross-sectional study, which is sort of derivational report action or a representative subset that is at a specific point in time. This methodology can be used to assess the burden of medication error or health needs of a population. Our result shows the frequency of medication error associated with the omission of medication are one time done by the total of 43 (36%) health care professional, and the other of 35 (29%) of participant done the errors two times, the errors done by 30 (25%) participants for 3 times, 11 (9%) workers done the errors 4 times, and the rest of 1 (1%) participant done the errors 5 times there is no one health care provider did the errors more than 5 times, according to the result of factors leading to medication errors shows that the errors done by 35 (29%) participants due to look alike medicine, as well the other 26(22%) health care professional took place the errors due to sound alike medicine, the remaining 59 participants in which the 27(22%) health care provider done the mistakes due to medicine used in rare cases, and the rest of 32(27%) health care workers done the errors due to using acronyms of drug names. According to our knowledge this is the first study in Pakistan to explore the erroneous views of nurses in the intensive care unit on medication. I believe it is necessary to provide continuous safe drug management training for ICU nurses in hospitals and the causes of drug errors and omissions should be investigated further.
Keywords: factors; types; medication errors; frequencies; health care providers
Introduction
The errors of medication are hazardous for patient’s safety as well as increase the expanses of hospitals. It is necessary to analyze the errors of medicine which help nurses and paramedic’s staff and hospital administration to investigate the occurrence of medication errors and the ways to prevent them. Many types of medication error such as, low and excessive dosage, giving medication of one patient to another, omission of medicine, medical factor such as lookalike medicine, sound alike medicine, medicine used in rare cases are most common among hospital staff [1]. A study carried in different countries covering 113 ICUs shows that the medication errors among ICUs staff are about 74%. The errors of medication commonly occur in Intensive Care Unit due to serious situation. The great consequence of mistake in medicine are the patient’s death ratio and as well as disease ratio. It may be affecting the ill person family and indirectly the health care professional by increasing cost of hospitals and stay of patients in the hospital for long time [2]. The medication therapy is mostly used in little babies and neonates; therefore, the drugs error mostly occurs due to age, weight, and insufficient drugs calculation skills or lack of pharmacological knowledge [3]. The greater part of the examination taking drugs mistakes has been directed in the USA and Europe. Data on the frequency of drug in low-income nations is constrained. We have concentrated on Middle Eastern nations so as to investigate and explore the issue of drug mistakes in this area. There is an assortment of reasons why medicine mistakes might be distinctive in this area [4]. In some other examine, they evaluated the drugs mistakes related to infusion pumps in intensive care unit. The prescription mistakes that were detected by means of one medical pharmacist in a nephrology ward, those stated studies confirmed the cooperation of clinical pharmacists and pharmacists with medical team were so beneficial [5]. During training, the particular perspectives of those different disciplines were shared to maximize appreciation of capacity error types and to expand a comprehensive, uniform technique for mistake detection [6]. The difficulty of identifying and classifying drug errors was addressed elsewhere in this issue. Drug errors are considered herein as "disorders that harm or could harm the patient during treatment [7]. The classical "safe" scientific ideas aim to balance the risks and benefits of a selected treatment however they also follow to more trendy scientific practices. The length of every patient’s live within the ward was assessed from the time of admission to discharge and was reported as length of stay (days) before and after the remark length [8]. The nurses are involved in pediatric care state that the main cause of medicine mistake is fatigue due to hard work and the ratio of nurses is less than the ratio of patients (58.08%). Most of the nurses (88%) use the notification system of medicinal mistakes. Some of the mistakes of medicine were not reported due to blaming of nurses in case of adverse effect for the patients (52.95%). Decrease of trust on nurses (50.45%) [9].
Material and Methods
The frequency of a medication error or other health related characteristics in a population at a given point in time. This methodology can be used to assess the burden of disease or health needs of a population. Lady reading hospitals are the tertiary health care system in Peshawar. There are large number of register nurses and paramedics, we divided preformed questionnaire they fill it with their experience as health care provider and give us data about how many times medication error to know the frequency and what is the factor and types of medication error in Peshawar. All cases of medication error that come to male and female nurses’ medical and emergency, Intensive care unit department lady reading hospital Peshawar all nursing staff that has valid Pakistan Nursing Council registration, and at least one year experience in health care areas. Only those staff nurses have been included in the study who is actively/directly involved in Patient Care at wards and emergency department. Those staff nurses will be excluded from the study that have some auditory or visual problem and were not treated during the period in which medication error have occur. And those nurses who don’t have experience or not registered such as students doing internship during their study period. Data were collected from registered nurses about the medication error which is done by the nurses during their one-year duty rotation. The consent was taken from the hospital director and also from respective head of the departments. We brief the nurses about our questionnaire and then we distribute the Performa among registered nurses and the data was collected with the help of premade Performa which were filled by the nurses according to their knowledge. Upon completion of data collection, data were coded, captured on Excel work sheet for analysis. Ethical approval is approved by the ethical committee and the Director of institute of paramedical sciences (IPMS) KMU Peshawar and also by hospital ethical committee.
Results
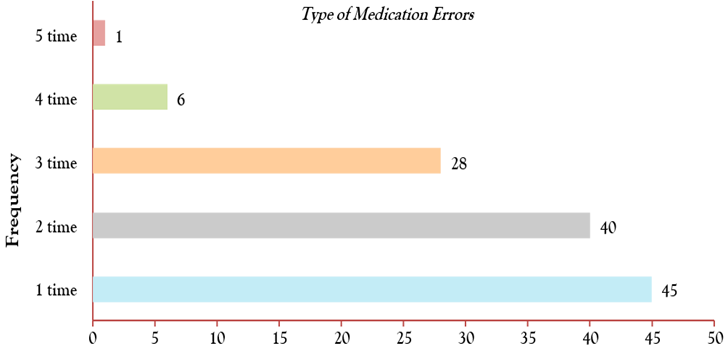
Total of 157 participants were included in this study in which both genders male and female, The 59 participants were male and the rest 98 were female. Out of 157 participants, 120 had done medication errors in the past year, while the rest 37 has not done any medication error in the past year. All of the frequency, types, and factors of medication errors are shown in below figures with sequence accordingly. There are the different types of medication errors occur in the hospitals and have the different situation which make prone the medication errors by the health care providers, such as nurses, paramedics and technologist of different specialties. As well as the main four factors that leads the medication errors by health care workers, which is explain with detail in the below figures. Figure 1 show the medication error which occurred due to giving medicine of one patient to another patient. The frequency of medication errors one time done by 45 participant, two times done by 40 participant, three times done by 28 participant and four times done by 6 participants as well as the medication error done by 1 participant 5 times respectively.
Figure 1: Medicine of one patient given to another.
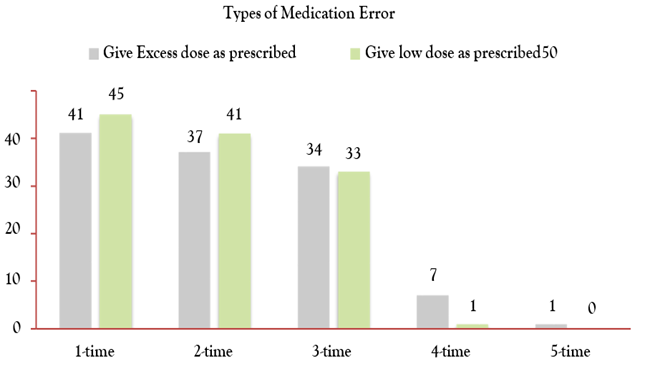
Figure 2 summarizes the frequency of medication errors due to excessive and low dosage as prescribed by the health care workers. the medication error of given excess dose as prescribed is done by the 41 participants for the first time 37 participant for the second time 34 participant for the third time 7 participant for the four times and the rest of 1 participant done this type of medication error for the fifth time.
Figure 2: Give excess and low dosage as prescribed.
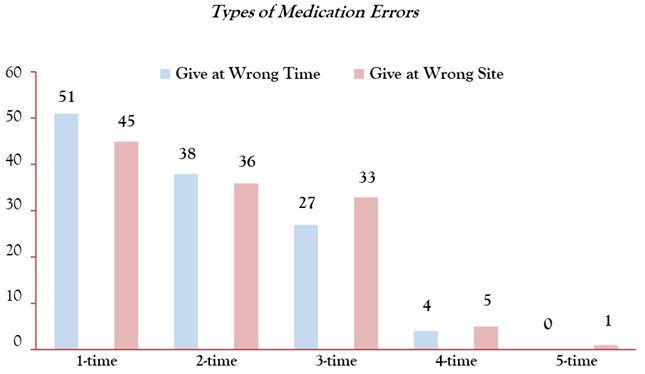
Figure 2 also show the type of medicine mistake give low dosage to the patients by health care provider the frequency of this type of medication error little bit different from the excessive dosage. As shown in the figure 2 the participant gives low dosage to the patients with different manner, the total of 45 participants did the error only one time and the other 41 participants did the errors two times, as well 33 participants done the error three times according to the figure result, there is only one participant who done the medication error four times in his past one year duty rotation, there is no single participant who did this error for five times in the duty rotation of past year. There are more than hundred types of medication errors in the health care setting which will difficult to analysis in the single research. But we have taken some of the medication errors and analyze it in the single piece of data from the participants who included in this study, the type of medication error which is related to the wrong time and site are as following in the figure 3 with detail, as we explained in the above section of material and method that we have included total of 157 people in this study and obtained the date from them through a sample of questionnaires, after collecting the data , we are analyze it through excel work sheet. The data shows that the type of medication errors which is related to administer of medicine at wrong time and also given at wrong site. In the figure 3 total of 51 health care workers take place the error of medicine given at wrong time is one time, 38 participants did the error 2 times, 27 people done the mistake 3 times and only the 4 participants done the error 4 times, and no one person did the medication error 5 time according to the figure 3.
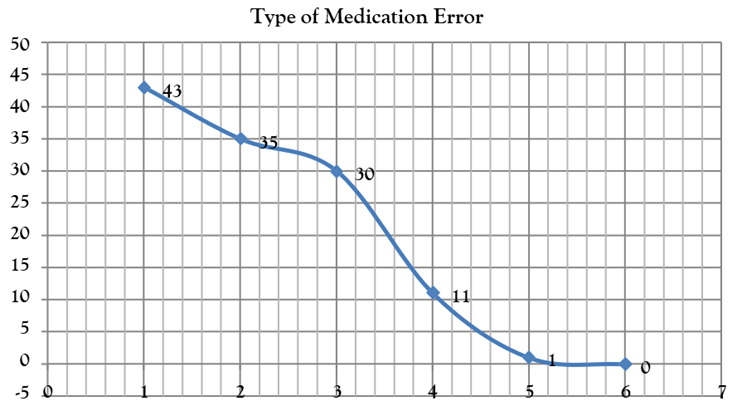
The major consequence of medicine administer through wrong route is the adverse effect in the health care system. It is very necessary to know about the route of administration of drugs. Due to lack of pharmacological knowledge the health care professional administer the drugs through wrong site and the result take place of adverse effect on the patients, in this research we have analyze this type of medication error which occur due to wrong site of administration, the total of 45 professional worker administer the drugs wrong site 1 time and the other 36 workers administer 2 times as well 27 persons given the medicine at wrong site for the 3rd time the other 6 participants in which the 5 participants give the medicine at wrong site for the 4th time and only one health care professional done the error 5 times respectively. The medication errors occur due to omission of medication, there is different reason of omission of medicine, like drugs not available, patients asleep due to medical condition, due to no availability of administration route, physician not prescribe on time and the prescription chart is left blank, patients’ rejection of medication, due to all of these reasons the medication doses may be omitted or may be delayed. The graph 1 shows that the 43-health care provider done this type of medication error one time. The remaining 77 participants in whom the 35 participants occur the error for 2 times the graph gradually low down from the ascending order to descending and the rest of 42 participants in which 30 professional workers done the error 3 times. The total reaming of 12 participants in which 11 done the error for 4 times and single participant done the error for 5 time, there is no one participant who did the error more than 5 times according to the graph one.
Graph 1: Omission of Medicine.
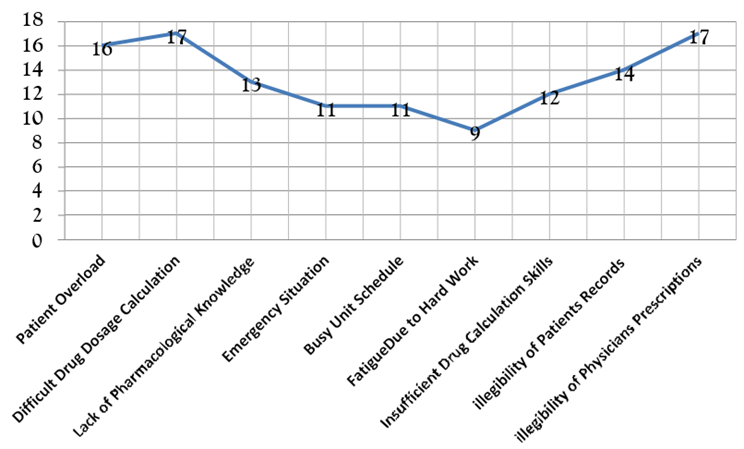
Those people who working in the hospitals such as Physician, Nurses, Paramedics, Allied health professionals, Respiratory therapist. They Have faced the different situation such as Patient Overload, Difficult drug Dosage calculation, Lack of pharmacological knowledge, Emergency situation, Busy unite schedule, Fatigue due to hard work, Insufficient drug calculation skill, Illegibility of patient’s records, Illegibility of physicians’ prescriptions. These situations make them prone to medication error. Here we discuss some of these situations with the proof of graph 2 result which prone the health care worker to medication errors.
As shown in graph 2 the total of 16 participants prone due to patients’ overload and done the medication error, the study was conducted in the lady reading hospital Peshawar which is one of the tertiary care institutes in the Peshawar Khyber Pukhtune Khwa Pakistan. All of the province patients depend on the institute, due to large concentration of patients, the ratio of patient’s is more to the health care workers due to overload of patients the health workers did the medication errors in different manner.
Graph 2: Following Situation Make Prone the Participant to Medication Errors.
Drug dosage calculation is one of the difficult processes in the field of medicine, due to the calculation of drugs the medication errors occur. Graph 2 summarize that total of 17 participants worried about drugs dosage calculation and did the medication errors, knowledge of pharmacology is the most important thing in the health care system the total of 13 heath care professionals done the medication errors due to lack of pharmacological knowledge according to the graph 2. Total of 11 participants done medication errors in the emergency situations. The remaining 63 participants in which the 11 participants done medication mistakes due to busy unit schedule as well as 9 professional workers fatigue due to hard work and done the mistake of medication. The rest of 43 participants in which the total of 12 participants did the medication mistake due to insufficient drugs dosage calculation the 14 participants done the errors due to illegibility of patients record and the rest of 17 participants take place the medication errors due to illegibility of physician’s prescriptions.
Factors Result of Medication errors
Studies have demonstrated that components, for example, medicine mistakes, absence of information and capability, and disregard of hospitals drug programs because of absence of time, extraordinary exhaustion, lacking work understanding, and unseemly workplace may all be identified with medication mistakes. Prescription mistakes are the most well-known errors of medication, which may bring about certain complication for patients. This examination was completed to research what impact medicine mistakes by attendants from their perspective.
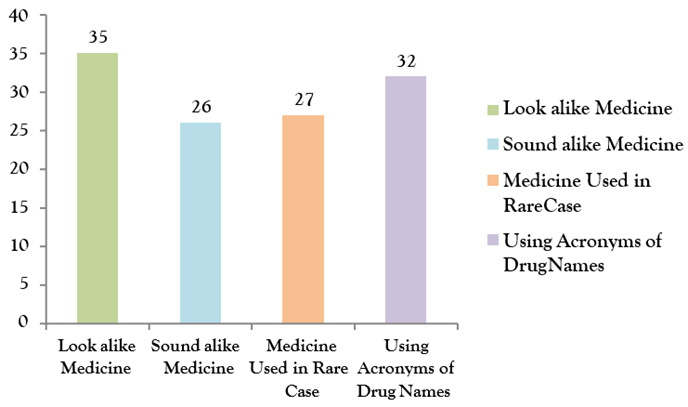
There are four main factors which is related to medication errors, such as lookalike medicine, sound alike medicine, that medicine which is used in rare cases, acronyms of drug names, here in figure four show that the total of 120 attendant of the study in which 35 participants done medication errors due to look alike medicine such as acetazolamide, acetohexamide, acetohexamide, acetazolamide, the 26 participants done the mistakes due to sound alike medicine for example olmesartan, valsartan, candesartan, 27 participants who was done the errors of medicine due to medicine used in rare cases, the rest of 32 health care workers done the mistakes of medicine due to using acronyms drugs names as shown in figure 4.
Figure 4: Medical Factors That Leads to Medication errors.
Discussion
The aims of this study to investigate the consequences of medication errors about the patients and as well for health care provider. The time of collecting the date we have to ask some important questions from health care provider who involve in this study. Every of the participant gave us different types of answer about our question. Majority of worker involved in the medication errors which are related to the types of medicinal errors such as medicine giving of one patient to another. Most of the professional worker doesn’t want to tell us about their mistakes due to personal reasons or due to hospital policy according to our point of views this is very important to set the medication errors notification system in the hospitals where the nurses ration is less than the patient’s ratio for the purposes to know about the medication errors which lead by health care workers. The result of done medication error is greater than those workers who did not done any medication mistake in the past one year of duty rotation. The total of 157 questionnaires distributed in which the 120 participants give us the data about done medication errors and other 37 participants answer a question mention in questionnaires with No about medication errors. The incidence of drug errors depends largely on human factors, and despite the latest developments in information technology and computer technology, it is not easy to monitor them. Medication errors can interferers the safety of patients and may increase morbidity and mortality. Compared with adults, pediatric patients are relatively vulnerable, which reflects their incomplete physiological development, so children are more vulnerable to the adverse effects of medication errors. Pediatric nurses play a key role in monitoring, notifying and avoiding medication errors. Therefore, the views of pediatric nurses about drug errors are an important basis for formulating strategies to avoid drug errors. Medical errors can be avoided, including errors related to drug management. Nurses are in a special position to ensure patient safety and avoid medication errors. Their views on patient safety deserve serious consideration. In this study, we summarized and analyzed the causes of pediatric nurses about medication errors, the methods used for error notification, and the opinions to avoid such errors. To date, few studies have addressed intensive care unit nurses' perspective on the causes of drug errors, reporting rates, and potential prevention strategies. As far as we know, this is the first study on this issue in Pakistan. Although the findings from the study cannot be generalized due to its small size, this study will help develop future research for intensive care unit nurses to develop causes and drug errors and potential care strategies.
Conclusion
Reporting drug errors to manage and reduce errors was a possibility for future medication errors. In this study, we reviewed the methods and rates of drug error reporting. Although in some cases the drug error notification is in writing, in most cases the notification is oral. Importantly, according to our research, only about half of medication errors require official notification. However, the rate of notification varies between different nurse groups. Intensive care nurses and nurses who care for 1 to 5 patients are noticed more frequently than service nurses or nurses looking for 6 to 10 patients. Thus, for example, in the intensive care unit, a reduction in the patient / nurse ratio can enhance primary care and improve the reporting of medication errors. Although oral notification is still an option for recording medication errors, it is important to increase the reporting rate by providing appropriate clear guidelines on error notification. According to the nurse's report, it is common to fail to inform about medication errors. The reasons cited by the ICUs nurse include that if the patient has adverse consequences, they may be accused of being a nurse, may lose the patient's trust, and may be condemned or disciplinary. Our vision the purpose of the study is to summarize outcomes and intervention plans. We investigated that the rate and severity of drug errors greatly increased from the reporting rate in previous study. The medical process is a complex system many opportunities for medication errors, our incidence of medication errors in general, similar to other ICUs the study uses a similar method of detection events. All categories and categories are identified with high prevalence. Error conveying and wrong drug routes Is an antibiotic and anticoagulant these results can be used to improve the quality of health care delivery.
References
- C. H. G. B. Ailey, B. R. S. E. Ngel, J. I. N. L. Uescher, M. A. L. T. Aylor, (2008). Medication Errors in Relation to Education & Medication Errors in Relation to Years of Nursing Experience Citations, J Nurs Res, 3:1-8.
Publisher | Google Scholor - A. Agalu, Y. Ayele, W. Bedada, M. K. Woldie, (2012). Medication Administration Errors in An Intensive Care Unit in Ethiopia, Int. Arch. Med, 5(1):15.
Publisher | Google Scholor - C. Mc Donnell, (2011). Opioid Medication Errors in Pediatric Practice: Four Years’ Experience of Voluntary Safety Reporting, Pain Res. Manag, 16(2):93-98.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Z. Alsulami, S. Conroy, I. Choonara, (2013). Medication Errors in The Middle East Countries: A Systematic Review of The Literature, Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol, 69(4):995-1008.
Publisher | Google Scholor - F. Dabaghzadeh et al., (2013). Medication Errors in An Emergency Department in A Large Teaching Hospital in Tehran, Iran. J. Pharm. Res, 12(4):937-942.
Publisher | Google Scholor - N. Jennane et al., (2011). Incidence of Medication Errors in A Moroccan Medical Intensive Care Unit, Int. Arch. Med, 4(1):32.
Publisher | Google Scholor - S. E. McDowell, H. S. Ferner, R. E. Ferner, (2009). The Pathophysiology of Medication Errors: How and Where They Arise, Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol, 67(6):605-613.
Publisher | Google Scholor - A. Valentin et al., (2009). Errors in Administration of Parenteral Drugs in Intensive Care Units: Multinational Prospective Study, BMJ, 338(7700):928-931.
Publisher | Google Scholor - E. K. Toruner, G. Uysal, (2012). Causes, Reporting and Prevention of Medication Errors from A Pediatric Nurse Perspective, Aust. J. Adv. Nurs, 29(4):28-35.
Publisher | Google Scholor