Research Article
Attitude Towards Moral Values in Relation to Self-Efficacy and Resilience Among Teacher Trainees
1Principal, Sravanthi College of Education, Warangal, Telangana (State), India.
2Assistant Professor, Dept of Education, National Sanskrit University, (A Central University), Tirupati (A.P), India.
3Research Scholar, Dept. of Education, Sun Rise University, Alwar, Rajasthan (State), India.
*Corresponding Author: K. Subramanyam, Principal, Sravanthi College of Education, Warangal, Telangana (State), India.
Citation: Subramanyam K, Naik M A, Jabeen S. (2024). Attitude Towards Moral Values in Relation to Self-Efficacy and Resilience Among Teacher Trainees. Addiction Research and Behavioural Therapies, BRS Publishers. 3(2);1-5. DOI: 10.59657/2837-8032.brs.24.020
Copyright: © 2024 K. Subramanyam, this is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Received: June 21, 2024 | Accepted: July 12, 2024 | Published: August 07, 2024
Abstract
Aim: Attitude towards moral values in relation to self-efficacy and resilience among teacher trainees.
Objectives: To examine the significant influence of self-efficacy and resilience on attitude towards moral values among teacher trainees and to find out the relation between self-efficacy and resilience with attitude towards moral values among teacher trainees. Sample: The present investigation consists of 400 teacher trainees in Chittor district of Andhra Pradesh state.
Tools: Attitude towards moral values inventory developed by Venkatrao & Soundararajan (2021), self-efficacy scale designed by Copeland and Nelson (2004) and Resilience scale established by Campbell-Sills and Stein (2007) were used.
Design: There are three independent variables like self-efficacy (low & high) and resilience (poor & good), each variable divided into two categories. Hence, a 2 × 2 factorial design was employed. Statistical Analysis: Mean, SD, ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) and Correlation were calculated. Conclusions: Teacher trainees with high self-efficacy have better moral values of their attitude than subjects with low self-efficacy. Teacher trainees with good resilience have better moral values of their attitude than subjects with poor resilience. There are significant positively relation between self-efficacy and resilience with moral values among teacher trainees.
Keywords: attitude towards moral values; self-efficacy; resilience and teacher trainees
Introduction
Facilitating learning is the process of education. It is the most effective method of bringing about the cultural, social and change in the economy required to achieve national objectives. People's moral, ethical, and spiritual values are promoted by it. It facilitates the conveyance of culture between generations. It facilitates the acquisition of the knowledge, abilities, morals, values, beliefs, and habits necessary for human existence. Productivity increases, emotional and national integration is achieved, and modernization progresses more quickly. Any educational system’s elements committed to educating and training teachers to move forward in the teaching competencies and skills in order to raise the Caliber of teachers within the framework is known as teacher education. Education and teacher training are not the same. While the knowledge, abilities, and attitudes gained during training are intended to enhance performance in a specific profession, the knowledge, abilities, and attitudes gained during education are general in nature and not specific to any one occupation. Training never happens in a vacuum. It involves material things, money, and people. However, the quality of the program, students, teachers, and instruction, resources or equipment, and overall management capacity (financial, administrative, and physical) are the five key factors that influence the output of training.
Every nation on the planet is going through a value crisis right now. In this sense, India is not an exception. It's been said that violence, cynicism, hypocrisy, exploitation, inequality, and disruption are all pervasive in today's social life. The current educational system bears a large portion to blame for this dismal state of affairs since it appears to be disconnected from human values, cultural heritage, and life realities. The purpose of education is to give children direction and resources for their growth, acknowledging that they make progress and excel in all areas i.e., physical, intellectual, emotional, ethical, and spiritual. The term “self-efficacy” is frequently used in relation to teacher training and development. Self-efficacy belief can be defined for specific fields. The belief that educators have in their capacity to plan and carry out the actions required to complete a given teaching task is known as teacher self-efficacy. Resilience in prospective teachers is the capacity to adjust to a range of environments and fortify skills in overcoming challenges. It constantly exhibits initiative, a sense of accomplishment, moral purpose, robust support networks, and excitement. The formation of resilience is dynamic and emerges when people integrate their personal and contextual resources and use practical techniques to overcome obstacles and maintain their wellbeing. It is affected by several psychological, biochemical, and environmental-contextual processes furthermore to individual features, familial factors, and the social context.
Literature Review
Qingzhi Heng and Lina Chu (2023) found that findings showed that work engagement was directly predicted by teacher self-efficacy, reflection, and resilience; additionally, teacher self-efficacy indirectly influenced work engagement through teacher resilience and reflection. In a similar vein, through teacher resilience, teacher reflection also indirectly influenced work engagement. Evgeniy Tufanov et al., (2023) observed that the outcomes of an empirical examination of the role that moral and spiritual values are relevant in the workplace of a contemporary Russian general education teacher. The role of general education as a significant social institution is to perpetuate the moral and spiritual values of the younger generation. developed strategic methods to get the pedagogical community ready for the challenges that come with the modern Russian society's demand that educational work and teachers’ values change. Ajay Kumar and Anita Kumar (2022) studied that they learn moral principles while they are in school. They will go on to hold significant positions as engineers, scientists, physicians, politicians, and businesspeople. Students in schools and colleges should be taught moral lessons in an appropriate manner. Moral principles provide us great satisfaction, self-assurance, and happiness. These values Mold us into kind, lovely people on the inside.
Hasan Kavgacı (2022) examined that the connections between the psychological toughness, teacher self-efficacy beliefs, and attitudes toward the teaching profession of aspiring educators. All of the research variables had significant and positive relationships with one another, according to the findings. The path analysis model's fit indices demonstrated how well the model fit the data. As a result, prospective teachers' attitudes toward the teaching profession and beliefs in their own efficacy are directly impacted by their psychological resilience. Furthermore, through their self-efficacy beliefs, prospective teachers’ psychological resilience also positively and indirectly influences their attitudes toward the teaching profession. Yi Wang (2021) made to methodically enhance and (re)create this quality in educators. Resilience in Chinese teacher education, which prioritizes pedagogical and financial issues over the socioemotional facets of teaching. It describes, in more detail, the background of teacher education in China, the definition and importance of teacher resilience, and a methodical approach to incorporating resilience into teacher education.
Timotheo Elinihaki (2020) examined that the prospective teachers in Tanzania have different ideas about the moral values that would supervising their education. These difficulties include the absence of values as a stand-alone subject, unsupportive settings like a dearth of instructional resources, uncooperative stakeholders like dishonest parents, and authorities who must ensure that policies, directives, and circulars are issued and carried out properly.
Augusta Muthigani (2019) explored the training of lecturers in Kenyan PTTCs to support teacher candidates’ values development. The findings called for a reconsideration of teacher education course pedagogy in able to put a renewed emphasis on the practical side of lecturers' development of values in PTTCs. Beng Huat See (2018) explored the moral values that young people believe in and the types of influences that mould their behavior. The results showed that young people comprehend moral principles quite well. Above all, they place a high value on honesty and trust. Courtesies and tolerance had less weight. Young people also exhibit a high degree of moral consciousness and an understanding of what characterizes a "good" person. Primary students were more likely than secondary students to view their teachers as significant moral role models and to have faith in them.
Vandana Chaturvedi and Kaushik (2018) found that the findings showed that there are no appreciable variations in the values of B.Ed. applicants who are aspiring teachers based on their gender or place of residence. Kaushik Bhakta and Nabanita Dutta (2017) examined that every part of a person's life is influenced by their values, including their speech, attire, discipline, etc. Moral and ethical values also influence how people respond to various situations, events, and circumstances. The findings are society’s responsibility to safeguard Indian youth so they will abstain from these immoral activities and meet life's challenges head-on and with courage. Kim and Lay (2017) showed that through teacher self-efficacy, resilience both directly and indirectly influences the stress level during teaching practice. Additionally, psychological resilience lessens stress during the teaching practicum, particularly by increasing self-efficacy in managing the classroom. It follows that the reduced stress encountered during the teaching practicum will positively influence the AtTP as well. This validates the study results regarding PR and TSE's impact on the AtTP. The results demonstrated that PR positively impacted TSE and that, via raising self-efficacy, PR both directly and indirectly strengthens the AtTP.
Rational of the study
Moral values will be properly instilled in students from an early age, and schools/colleges are the institutions most suited to fulfil this responsibility. As a result, it is imperative that research on moral values begin. One of the current social viruses impacting Indian society is a decline in moral values in the public, private, corporate and ideological spheres. This leads to terrorism, violence, corruption, and a rat race in the political and academic spheres. The study’s findings about teacher trainees’ attitudes toward ethical/moral values in connection to resilience and self-efficacy are extremely important.
Objectives
- To examine the influence of self-efficacy and resilience on attitude towards moral values among teacher trainees.
- To find out the relation between self-efficacy and resilience with attitude towards moral values among teacher trainees.
Hypotheses
- There would be significant influence of self-efficacy on attitude towards moral values among teacher trainees.
- There would be significant influence of resilience on attitude towards moral values among teacher trainees.
- There would be significant relation between self-efficacy and resilience with attitude towards moral values among teacher trainees.
Method
Participants
The present investigation consists of 400 teacher trainees both male and female studying in B.Ed., colleges in Chittoor district of Andhra Pradesh state was obtained as sample and by using systematic random sampling technique in the age group of 19-21 years.
Variables
Dependent Variable
- Attitude Towards Moral Values
Independent Variables
- Self-Efficacy
- Resilience
Instruments
Assessment of Attitude Towards moral values: Attitude towards moral values inventory developed by Venkatrao & Soundararajan (2021), which consists of 60 statements. The reliability of the inventory is established by test-retest method, it is 0.93 and validity of the instrument is 0.78.
Assessment of Self-Efficacy: The self-efficacy scale was developed by Copeland and Nelson (2004), which consists of 16 items. The reliability of this scale has been established by test-retest method, it is 0.82 and validity of the scale is 0.92.
Assessment of Resilience: Resilience scale established by Campbell-Sills and Stein (2007). The study utilized the 10-item. The scale has been established by Cronbach’s alpha is 0.80.
Design
The 3 variables i.e., self-efficacy (low & high) and resilience (poor & good), each variable divided into two categories. Hence, a 2 × 2 factorial design was employed.
Statistical Analysis
The Means and SDs of the scores were calculated. To find out whether there are any significant differences between the data was analysed ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) and Correlation were calculated.
Results
Table 1: Mean & SD of attitude towards moral values scores.
| Resilience | Self -Efficacy | ||
| Low | High | ||
| Poor | Mean | 173.58 | 193.34 |
| SD | 19.85 | 18.63 | |
| Good | Mean | 183.13 | 195.86 |
| SD | 16.89 | 17.79 | |
Grand Means
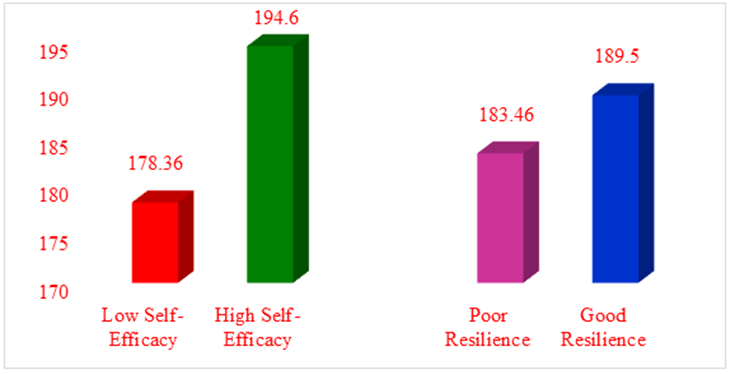
Low Self-Efficacy: (M=178.36); High Self-Efficacy: (M=194.60)
Poor Resilience: (M=183.46); Good Resilience: (M=189.50)
Table 1 shows that teacher trainees with high self-efficacy and good resilience (M=195.86) are better moral values of their attitude compared other groups. The subjects with low self-efficacy and poor resilience (M=173.58) are better moral values of their attitude when compared other groups. Grand means reveals that in terms of self-efficacy, the subjects with high self-efficacy (M=194.60) are better moral values of their attitude than the subjects with low self-efficacy (M=178.36). In terms of resilience, subjects with good resilience (M=189.50) are better moral values of their attitude than the subjects with poor resilience (M=183.46).
Figure 1: Graphical Representation for moral values based on independent variables.
Table 2: ANOVA for the scores on attitude towards moral values.
| Source of Variance | SS | df | MSS | ‘F’-Value |
| Self - Efficacy (SE) | 985.230 | 1 | 985.230 | 7.08** |
| Resilience (R) | 895.125 | 1 | 895.125 | 6.44** |
| SE × R | 795.126 | 1 | 795.126 | 5.71* |
| Within | 55092.708 | 396 | 139.123 | - |
| Total | 57768.189 | 399 | - | - |
**-Significant beyond 0.01 level; *-Significant at 0.05 level
The above table clearly indicates that the ‘F’ value is 7.08 for the variable self-efficacy is significant beyond 0.01 level suggesting that teacher trainees have better moral values. Teacher trainees with high self-efficacy (M=194.60) are better moral values of their attitude than teacher trainees with low self-efficacy (M=178.36). The ‘F’ value of 6.44 for the variable resilience is significant at 0.01 level suggesting that teacher trainees have better moral values. Teacher trainees with good resilience (M=189.50) are better moral values of their attitude than teacher trainees with poor resilience (M=183.46). The ‘F’ value of 5.71 for the interaction is significant. It indicates that the interaction effect between self-efficacy & resilience on attitude toward moral values.
Table-3: Shows Pearson’s co-efficient correlation between self-efficacy and resilience with attitude towards moral values among teacher trainees.
| Variables | ‘r’-Values |
| Self-Efficacy & Moral Values | 0.053 |
| Resilience & Moral Values | 0.029 |
Table 3 Indicates a significant positive correlation of 0.053 between self-efficacy and moral values. Also, a positive correlation of 0.029 between resilience and moral values among teacher trainees.
Discussion
The first hypothesis stated that there would be significant influence of self-efficacy on attitude towards among teacher trainees. The ‘F’ value for self-efficacy to influence of attitude towards moral values is significant. For prospective teachers, having a high level of self-efficacy—which is referred to as psychological capital is a crucial advantage. The human relations-focused nature of teaching makes it more likely for burnout to occur, which emphasizes the importance of having strong psychological capital. Thus, it can be said that this resource will help candidates as they advance in their careers. These findings are corroborated with the earlier researchers of Hasan Kavgacı (2022) and Qingzhi Heng and Lina Chu (2023) who also found significant influence of self-efficacy on moral values. Based on the results the hypothesis-1 is accepted. The second hypothesis stated that there would be significant influence on attitude towards moral values among teacher trainees. There is significant influence of resilience on moral values. Its goal is to prepare aspiring teachers for the challenges that lie ahead in their career by strengthening their resilience. It also offers valuable insights into how to cultivate this quality in pre-service education through learning communities. Teacher candidates are better equipped psychologically to handle some of the cultural challenges of the profession thanks to their practicum, which gives them real-world experience in the classroom, and their learning communities, which allow them to share their teaching experiences with one another. These findings are corroborated with the earlier researchers of Yi Wang (2021) who found that the significant influence on moral values of their attitude, hence the hypothesi-2 is accepted. The third hypothesis stated that there would be significant relation between self-efficacy and resilience with attitude towards moral values among teacher trainees. There are significant positively relation between self-efficacy & moral values and resilience & moral values, hence the hypothesis-3 is accepted.
Conclusion
Teacher trainees with high self-efficacy have better moral values of their attitude than subjects with low self-efficacy. Teacher trainees with good resilience have better moral values of their attitude than subjects with poor resilience. There are significant positively relation between self-efficacy and resilience with moral values among teacher trainees.
References
- Ajay Kumar and Anita Kumar. (2022). Importance of moral values in student life. International Journal of Creative Research Thoughts, 10(10):c582-c588.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Augusta Muthigani. (2019). Values development in teacher trainees: implications for lecturers in primary teacher training colleges in Kenya. Educational Planning, 26(2):47-54.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Beng Huat See. (2018). Understanding the Moral Values of Young People and the Key Influences on their Character Development. Interdisciplinary Education and Psychology, 2(2):1-32.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Evgeniy Tufanov, Juliya Lesnykh, Inna Kravchenko, Ludmila Zvereva, and Valentina Ivashova. (2023). Spiritual and moral values in the professional culture of a modern teacher. E 3S Web of Conferences 420.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Hasan Kavgacı. (2022). The Relationship Between Psychological Resilience, Teachers' Self-Efficacy and Attitudes Towards Teaching Profession: A Path Analysis. International Journal of Progressive Education, 18(3):278-296.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Kim, N., & Lay, Y. (2017). The relationship between resilience and perceived practicum stress: The mediating role of self-efficacy. Sains Humanika, 9.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Qingzhi Heng and Lina Chu. (2023). Self-efficacy, reflection, and resilience as predictors of work engagement among English teachers. Front. Psychol, 14:1160681.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Vandana Chaturvedi and N.K.Kaushik. (2018). A study of values of B.Ed., students with respect to gender and locality. International Research Journal of Human Resources and Social Sciences, 5(11):1-6.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Yi Wang. (2021). Building Teachers' Resilience: Practical Applications for Teacher Education of China. Sec. Educational Psychology, 12.
Publisher | Google Scholor