Research Article
Analysis of Conservative Versus Surgical Treatment in Fractures Diaphyserias of Third Average from The Clavicle: One Revision Systematics with Metanalysis of Clinical Trials Randomized
- Bianca G. Oliveira 1*
- Luiza Nunes Forattini Lima 2
- Helena Rocha Souza Dias 3
- Thiago Santos Silva 4
- Mayra Rocha Santos Freire 5
1Medical student at Universidade Salvador, Salvador, BA, Brazil.
2Resident in Orthopedics and Traumatology at Hospital Estadual Jayme Santos Neves, Serra, ES, Brazil.
3Resident tip at Centro Medico de Campinas, Campinas, SP, Brazil.
4Resident doctor at Hospital Sao Francisco, Ribeirao Preto, SP, Brazil.
5Resident tip at Hospital Metropolitano, Cuiabá, Mato Grosso, Brazil.
*Corresponding Author: Bianca G. Oliveira, Medical student at Universidade Salvador, Salvador, BA, Brazil.
Citation: Oliveira B.G., Lima L.N.F., Dias H.R.S., Silva T.S., Freire M.R.S. (2024). Analysis of Conservative Versus Surgical Treatment in Fractures Diaphyserias of Third Average from The Clavicle: One Revision Systematics with Metanalysis of Clinical Trials Randomized, Journal of Clinical Research and Clinical Trials, BioRes Scientia Publishers. 3(4):1-8. DOI: 10.59657/2837-7184.brs.24.034
Copyright: © 2024 Bianca G. Oliveira, this is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Received: September 02, 2024 | Accepted: October 25, 2024 | Published: November 01, 2024
Abstract
Introduction: To compare plate fixation and conservative treatment of deviated fractures of the middle third of the clavicular diaphysis in relation to healing, pseudoarthrosis, adverse events and shoulder function.
Methodology: Systematic review with meta-analysis carried out using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) criteria. The search was carried out in the databases (MEDLINE and LILACS) and the SPICE6 strategy was used to identify the relevant studies.
Results: 496 patients were included, of whom 252 talked conservative treatment for fracture of the middle diaphyseal third of the clavicle and 244 surgical treatments, with primary open reduction and plate fixation. The studies analyzed in this systematically review showed better results in the Constant and DASH (Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand) assessments in the surgical group.
Conclusion: Surgical treatment for the of diaphyseal fractures of the middle correction third of the clavicle is superior to conservative treatment, to the it reduces rates of pseudoarthrosis, improves range of movement, faster return I'm activities and greater patient satisfaction.
Keywords: clavicle; diaphyseal fracture of the clavicle; clavicle surgery; conservative treatment
Introduction
Fractures in clavicle have one prevalence in 2.6% in all to the fractures in young people active. Diaphyseal fractures of the middle third make up 80% of all fracture’s clavicular injuries, which makes scientific research on treatment important. The high occurrence of symptomatic consolidation and pseudarthrosis after non-operative treatment of Displaced diaphyseal fractures of the middle clavicular third suggest a surgical indication for this pathology [1].
Displaced fractures of the clavicular middle third have a pseudoarthrosis rate of 15% and 31% of unsatisfactory results. Therefore, the consolidation of the bone fracture in question stands out for clinical and radiographic characteristics important for therapeutic management. Surgical fixation has shown better functional results and a better rate of consolidation and pseudarthrosis in comparison with non-operative treatment in one year of follow-up [2].
Studies regarding surgical treatment of clavicular fractures are under discussion in community scientific, visa what, despite of the results varied, exist one trend in manage diaphyseal fractures of the middle third of the clavicle early with open reduction primary and plate fixation. Resulting or not in better outcomes for patients described and evaluated based on the high prevalence of symptomatic consolidation. In addition to high values reported in pseudarthrosis after O treatment no operative [3-5].
Most common etiology associated with falling on the shoulder or with an outstretched arm and association directly involving sports and bicycle accidents. Mechanism evaluation and quantification exact trauma and kinetic energy involved are important signs for suspicion and diagnosis precocious. Since, the therapeutic indication is based on anatomical involvement and deviation. To the simpler are usually treated conservatively and the more unstable and deviated must to be treated surgically [3-5].
It should be noted that the presence of additional injuries and patient-related factors require be considered for individualized therapeutic decision-making. Therefore, the objective of this study was to compare plate fixation and conservative treatment of displaced fractures of third average from the diaphysis clavicular in relationship The consolidation, pseudarthrosis, events adverse and shoulder function.
Methodology
Systematic literature review, with quantitative-qualitative approaches to the collected data, whose structuring if it gave according to the guidelines in Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA)5 subsequently being structured a list in verification for analyzing the results. For detailed data analysis, a diagram was used. four-step flow.
The search for studies that met the established criteria took place in March/2024 in bases in data linked The Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online (MEDLINE) and Latin American and Caribbean Literature in Health Sciences (LILACS), using the strategy SPICE ⁶ for identification of the studies relevant:
- Setting (Scenario): patients with FRACTURES CLOSED OF THIRD AVERAGE DIAPHYSEARY FROM THE CLAVICLE.
- Perspective (Perspective): To compare treatment surgical It is conservative in fractures closed of middle diaphyseal third of the clavicle.
- Intervention (Intervention): Surgical correction and conservative treatment.
- Comparison (Comparison): Reduction of Detour, improvement from the pain, improvement from the quality in life and function BIOMECHANICS.
- Evaluation (Assessment): Rate or occurrence in recurrence of Detour and/or gets worse from the function locomotor (range of movement).
Your descriptors in sciences from the health (DECS) / MESH TERMS they were used in form combined, according to the following structure:
FRACTURES FROM THE DIAPHYSIS AVERAGE FROM THE CLAVICLE AND Surgery Orthopedic (Orthopedic procedures).
Subsequently, the studies were sorted according to the theme addressed, restricting themselves to studies what versed about the correction surgical from the FRACTURES FROM THE DIAPHYSIS AVERAGE FROM THE CLAVICLE.
Inclusion Criteria
They were included at the study patients what present (1) fracture diaphyseal average completely diverted from the clavicle (without contact cortical in between your main fragments proximal and distal), (2) fracture in the middle third of the clavicle (fracture capable of fixation with a minimum of three screws in each proximal and distal fragment), (3) age between sixteen and sixty years of age, (4) absence of medical contraindications to general anesthesia and (5) consent informed.
Exclusion Criteria
Patients aged less than sixteen years or older than sixty years, (2) fracture in the proximal or distal third of the clavicle, (3) pathological fracture, (4) fracture open, (5) fracture observed more than twenty-eight days after injury, (6) neurovascular injury associated with finds neurological goals to the exam physicist, (7) one trauma associated cranioencephalic disease (a Glasgow Coma Scale score of <12>
The search and selection of studies was carried out by two reviewers who independently carried out the analysis of studies. Initially, using the mentioned DECS, together with operators Booleans they were selected studies published us last five years (2018-2023) followed by analysis of titles and abstracts. At this stage, studies with animal models, opinion articles, studies that did not consider the surgical approach to EIA, good such as literature reviews.
Once this stage was completed, the full texts of the articles were recovered for analysis of the other inclusion and exclusion criteria. Duplicate citations and studies that were not correspondents to the parameters revisional proposed. Possible disagreements they were resolved through discussion with a third reviewer, with inclusion decided after consensus with the two main reviewers.
Extraction epidemiological and Demographic Data
Executed through the creation of a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet, including parameters such as number of patients, initial and final degree of curvature (deviation) of the middiaphyseal fracture of the clavicle, treatment strategies, relapses, complications, results obtained.
The systematic review protocol was registered in the International prospective register of systematics reviews (PROSPEROUS) under CRD42024549732 aiming better quality It is adequacy of the results to proposed objectives.
Results
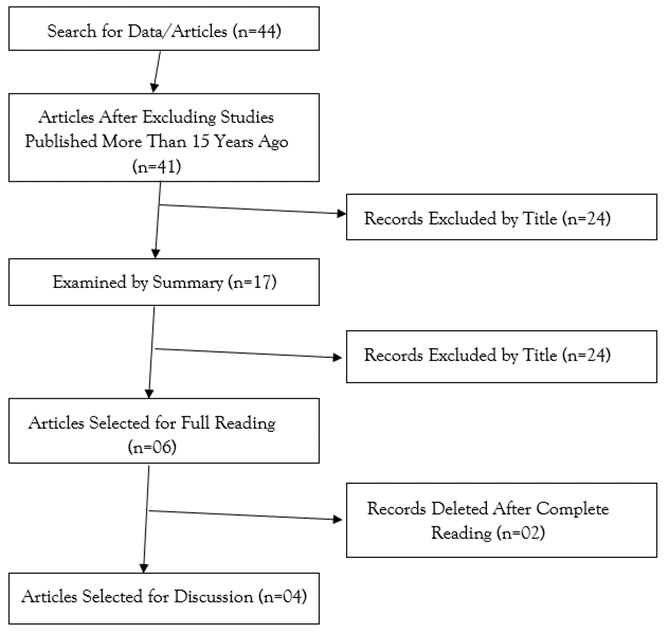
They were selected 44 articles during O process in search, after the exclusion those published more than 15 years ago, 41 remained. analysis of the title and abstract allowed the exclusion of 38 works that did not correspond to the objective of this study. A complete reading of 06 articles, of which 02 were excluded for not meeting the inclusion criteria, finally, 04 they were selected for the construction of the article (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Studies selected according to PRISMA methodology.
Source: Own authorship (2024).
The 04 selected articles presented patients diagnosed with fractures of the middle third clavicle shaft who underwent conservative or surgical treatment, with reduction primary and plate fixation (ORIF). Functional assessment was carried out using Constant and disability assessment with Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) reported in some studies. 496 patients were included, of which 252 underwent treatment conservative for fracture of the middle diaphyseal third of the clavicle and 244 by surgical treatment, with primary open reduction and fixation with plate.
A table 1 it presents you articles selected It is your results obtained [7-10].
A table 2 punctuation after 01 year in fixation with the plate it is screw [7-10].
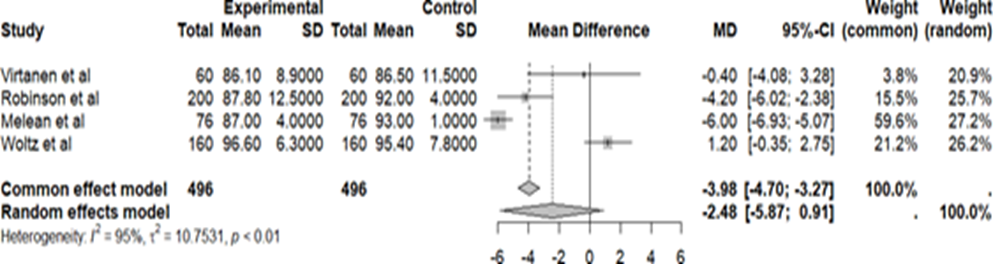
A figure 2 it presents O graphic forest with the punctuation in constant of the studies selected [7-10].
Table 1: Results obtained by the studies selected.
| Study | Approach | Patients F/M | Results |
| Virtanen et al | Treatment conservative Fixing with plate | 8/52 | Constant scores; Scores disability with DASH; Pain or VAS; Fracture consolidation; Complications; Non-union analysis |
| Robinson et al | Treatment conservative Open reduction and fixing with plate | 25/175 | Healing of fractures; Result scores functional, Constant and DASH; Scores subjective and range of motion reported by the patient; Removal from work and sport; Other events adverse events and complications; General summary of secondary operative treatment; Evaluation economic. |
| Melean et al | Treatment conservative Open reduction It is fixation internal | 76 *This one work no specific u! | Complete return to work time; Clavicle shortening; Constant; Signals radiological findings of bone consolidation. |
| Woltz et al | Treatment does not operative Open reduction and fixing with plate | 14*/146 | Healing of fractures; Functional results, DASH and Constant; Secondary operations; Other adverse events; Score SF-36; Painand cosmetic results. |
Table 2: Punctuation Constant/DASH after 1 year in fixation with plate versus treatment conservative.
| Punctuation | Study | Sample | Middle Ages | Treatment Does Not Operative | Treatment Operative |
| Constant | Virtanen et al | 60 Patients | 33 Years to Not Op; 41 Years for Op | 86.1 (8.9) | 86.5 (11.5) |
| Dash | Virtanen et al | 60 Patients | 33 Years to Not Op; 41 Years for Op | 7.1 (13.5) | 4.3 (6.1) |
| Constant | Robinson et al | 200 Patients | 2.5 Years to No Op; 32.3 Years to Op | 87.8 ± 5.1 (85.2 - 90.3) | 92.0 ± 4 (90.0 - 94.0) |
| Dash | Robinson et al | 200 Patients | 32.5 Years to No Op; 32.3 Years to Op | 6.1 ± 4 | 3.4 ± 3 |
| Constant | Melean et al | 76 Patients | 37.2 ± 11.2 Years for Non-Surgical; 38.1 ± 13 Years for Op | 87 (79-95) | 93 (91-95) |
Figure 2: Forest Chart with The Constant score of the selected studies.
For O study in Virtanen, it is col [7], 32 patients participated of group in treatment conservative and 28 from the surgical group, but only 51 patients completed 1 year of follow-up, 09 patients were lost to follow-up, 07 from the non-operative group and 02 from the operative group. As for the mechanism of trauma,19 by fall; 25 per bike; 04 due to car accident; 09 for sport and 03 for skiing. The Constant score in the non-operative group was 86.1 (8.9- standard) and in operating group 86.5 (11.5- deviation standard) (P=0.90). Already DASH score, 7.1 ± 13.5 and 4.3 ± 6.1(P=0.81), respectively. On the pain scale or VAS, 7(18.6 - standard deviation) in the group non-operative and 3(6.0- standard deviation) in the operative group (P=0.88). All fractures in the group operative fractures consolidated, but only 19 (76%) of the 25 fractures in the non-operative group had consolidation(P=0.01), you 06 patients after failure of treatment conservative they were treaties surgically (P=0.61). Registered 19 complications, 12 at the group no operative It is 07 at the surgery (P=0.15), no serious complications or wound infection. In the non-operative group, occurred 01 case in delay at consolidation, 02 cases in bad unity symptomatic with shortening > 20mm, angulation or displacement of the clavicle (P=0.24), 02 cases of refracture and 01 case of irritation of the brachial plexus (paresthesia, pain and sensation of weakness) (P=0.49). In the operative group, 03 cases of delayed consolidation, 01 case of loss of reduction due to flexed plate, 01 case device breakage, 01 case of skin irritation, 01 case of refracture. In the analysis of no consolidation at the group no operative showed one difference important at the displacement at baseline between united and non-united fractures(P=0.009), all fractures displaced <1>1.5 width were not consolidated.
At the rehearsal clinical randomized in Robinson, et al [8], 105 patients they were treaties in mode conservatively and 95 surgically, with open primary reduction and plate fixation. About the mechanism in trauma,80 patients they were due the sport, 51 due the bicycle It is motorcycle, 44 due to simple falls, 20 due to aviation accidents, 5 due to other causes. Only 178 patients completed 01 year in follow-up, 92 patients (87.6%) of group no operative It is 86 patients (90.5%) in the surgical group, 22 were lost to follow-up. Regarding the consolidation of fractures, 24 patients (26.1%) of group no operative had fractures what no they were radiographically united at six months, of these, 16 with pseudarthrosis, of which 13 were underwent surgery, and 08 had late consolidations, between six and twelve months. Already in the group operatively, 01 (0.1) of the 86 patients did not exhibit union, with no record of late unions. The risk of nonunion was significantly lower in the surgical group, with a 93% reduction in risk when compared with O treatment conservative (p=0.007). Furthermore, O smoking he was associated with nonunion (p=0.006). Regarding the mean functional scores of Constant and DASH was better in the operative group than in the non-operative group in all evaluations. Constant score was 92.0(90.0. to 94.0) in the operative group and 87.8(85.2 to 90.3) in the non-operative group. operative (P=0.01). In DASH, the average was 3.4 (1.9 to 4.9) and 6.1 (4.1 to 8.1), respectively (P=0.04). About the assessment subjective It is amplitude of the movements, The dissatisfaction how much The prominence bone clavicular at the local from the fracture he was reported per 26 patients of group conservative It is 5 of surgical group, (P=lessthan0.0001); asymmetry of shoulder, 17 It is two patients, respectively (P=lessthan0.0001); fall of shoulder, 15 It is 1 patients, respectively (P=lessthan0.0001); sensitivity/irritation local, 11 It is 17 patients, respectively (P=0.2) It is numbness local, 4 It is 15 patients, respectively (P=0.006). No there was differences important in between you two groups in terms in amplitude in movement active or shoulder passive. 10 patients (12percentage) in the surgical group underwent removal of the plate after bone consolidation. Regarding absence from work and sport, there was no large differences between the two groups in terms of total time absent from work after the fracture (p=0.7). Among the 142 patients who practiced sports before the trauma, there was also no important differences between the groups in terms of the number of patients who returned or how much to the time for return. In relationship the events adverse It is complications, at the group operatively, 03 underwent excision of the bony prominence at the site of the injury, 02 reported painful clicking in the sternoclavicular joint and 01 underwent surgery due to pain persistent even with consolidation. In the surgical group, 02 with mechanical neck pain and dysesthesia in the arm, 02 suffered new fractures lateral to the plate and 01 presented flexion of the plate. No record of intraoperative complications, postoperative neurological deficits or infections deep. Only 02 used oral antibiotics due to superficial infection, 01 had dehiscence partial suture and 03 developed impingement on the rotator cuff(01 from the conservative group and 02 of surgical).About of treatment operative secondary, at the group no operative, 17 patients(18.5%) underwent surgery in the first year(13 due to non-union, 03 due to excision of bony prominence and 01 due to malunion); In the surgical group, 16 patients (18.6%) were subjected to secondary interventions(10 for plate removal, 02 for fractures lateral to the plate, 01 due to non-union, 01 refracture after plate removal and 01 folded plate and impact symptoms). Regarding the economic evaluation, initially the expenses in the surgical group they are bigger, but in the following year the injury is higher in the conservative group (P=0.00001).
In the study by Melean et al [9], 41 patients were treated conservatively and 35 patients through surgery. Full return-to-work time analysis achieved sooner at the group operative (2.9 ± 0.8 months) of what at the group no operative (3.7 ± 1.1 months, P=0.003). In relation to fracture deviation, the values did not differ so much, with average results 19.3 ± 7.8 mm for the non-operative group and 21.4 ± 6.1 mm for the operative group (P=0.533). About O shortening clavicular after the fracture, he was similar in between your groups, with one mean shortening of 7.5 ± 7 mm for the non-operative group and 9 ± 9.8 mm for the surgery (P=0.450). The Constant score in the non-operative group was 87(79-95) and operative 93(91-95), with one punctuation average in 6 points higher what O another group (P=0.003). You signal radiological in consolidation at tomography computerized to the 6 weeks they were present in 5.3% of patients in the non-operative group and 24.1% in the operative group (P=0.005), already to the 12 weeks, 16.7% of the patients It is 81% patients, respectively (P=0.004). 04 patients (9.6%) with pseudarthrosis in the non-operative group, who underwent reduction open and fixation with plate and additional bone allograft and other 04 patients (11.7%) in the group operative removed the implant due to symptomatic plate or screws, with no record of failure union in this group.
The randomized multicenter study by Woltz et al [10], with 160 patients, 74 from the non- operative group and 86 from the operative group, from the first group 01 patient due to pain underwent surgery. Regarding the mechanism of trauma, 73 due to traffic accidents; 66 per sport; 5 per falling from a height and 14 from other causes. After 1 year, 18 patients did not undergo an x-ray, 06 had previously achieved consolidation, 06 contacted reported that they had excellent function, without pain or other complaints and 06 were lost to follow-up before the status was determined in unity It is no could to be contacted. To the end in 01 year, 02 patients (2.4%) of group operative and 15(23.1%) of the 65 patients in the non-operative group with radiography available, had developed pseudarthrosis (P=0.0001). The Constant score, 96.6 ± 6.3 in the non-union group, operative It is 95.4 ± 7.8 at the group operative (P=0.35). Already O DASH, 3.2 ± 7.4 It is 4.5 ± 7.6, respectively (P=0.30). 11 patients (15.7%) of group no operative they were submitted the surgery due to adverse events, 09 due to non-union; 01 poor union and 01 complications late neurological disorders. In the surgical group, 09 patients (10.7%) underwent a new surgery, 02 due to deep wound infection, 05 due to early implant failure, 01 late failure and 01 not consolidation with refracture after the removal of implant. How much the others complications perioperative conditions, cephalic vein thrombosis, superficial wound infection and cardiovascular events. Big part of the patients’ treaties surgically reported paresthesia from the skin the return from the scar during follow-up, persisting in 15 (19.2%) of the 78 patients. The score of SF-36 was lower in the non-operative group (P=0.03) only at six weeks. The scores of pains were slightly greater in the conservative group, but only at six weeks and 5% of patients of group operative reported dissatisfaction with O result aesthetic after one year (P=0.06).
Discussion
An assessment per constant it is disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand (DASH) evaluated the functional capacity and shoulder disability, all studies used for analysis, the patients with fixation with plate presented scores lightly best when compared to the non-operative group, but the clinical relevance of this difference is unclear. A fixation with plate he was also related the one consolidation faster, with better analysis radiograph, faster return to work and exe rise, lower pain scores, and lower need for reapproaches [7-10].
These fractures are common and typically occur in younger patients, meaning a problem for it is population more active. Traditionally, these fractures of third average clavicle shaft are treated conservatively, with a sling or bandage figure eight shape, with expectations of a high possibility of fracture consolidation, excellent functional results and a good level of patient satisfaction. However, the non-consolidation of clavicular fractures and treated conservatively happens more regularly than if thought. Because of this, surgical treatment methods have been applied to this type of fracture, mainly comprising fixation with plate [11-13].
There is still no consensus on the preferred treatment for displaced shaft fractures. clavicle, however, the procedure performed, whether surgical or not, aims at complete improvement from the function of shoulder, especially in patients more young people. Nonetheless, many studies show a high risk of pseudarthrosis after conservative treatment, raising a further role most important part of the treatment operative [11-15].
Data found in another study state that 14% of the 452 patients studied in the group in treatment conservative developed pseudarthrosis, O what It is substantially higher of than the patients evaluated in the operative group. It has also been reported by other researchers, through Constant and DASH scores that later after a year there is better stabilization from the fracture after the fixation in plate of what after O treatment conservative. Post that, to the compare surgical and non-surgical treatments, operative treatments provide greater chance of consolidation, reducing the risk of pseudarthrosis and leading to a faster recovery rapid fracture [11-15].
Regarding the advantages of surgical treatment, it is concluded that it produces a greater chance of consolidation in one year of follow-up of adult patients with this type of fracture of clavicle, effectively reducing the rates of pseudarthrosis, symptomatic malunion, neurological symptoms and general complications. On the other hand, there are some disadvantages that should be mentioned, such as skin infection and irritation, numbness around the scar surgery because of possible injury to the branches of the cutaneous supraclavicular nerve and risk of refracture after removal from the plate. At the however, mostly, the fixation from the plate offers clear advantages, and is an excellent option for patients who need a recovery faster and for patients with risk factors for pseudarthrosis, such as fracture and smoking [12,14,16,17].
O contour It is the anatomy from the clavicle they are bent over in several plans, due the that, several studies analyze the conformation anatomical of that bone for what O treatment surgical with the fixation from the plate be likely to be adjusted with bigger precision the anatomy in form in "S" from the clavicle. When compared to the treatment conservative, the fixation from the plate decreased significantly the rate in no consolidation post-operative, resulting in one improvement functional. Regarding stability, it was analyzed in other studies that the compression plate in the reconstruction plate provides better results in this regard. When evaluating scores functional, there was one improvement in one year at the score DASH in relationship to the interventions surgical, you which got one classification higher in relationship to the treatment’s conservatives. It is concluded that patients treated with plate fixation can achieve full range of motion [12,14,16,17].
Conclusion
It is concluded that treatment must be based on shared decisions, related to therapeutic advantages and disadvantages, which need to be informed by professionals. A Surgical approach with open primary reduction and plate fixation is superior to conservative in displaced fractures of the middle diaphysis of the clavicle of the middle diaphyseal third of the clavicle. Visa that, surgery potentially reduces rates of pseudarthrosis, increases the likelihood of bone consolidation, range of motion, faster return to work and greater satisfaction of patients. Therefore, it is important that the choice is based on shared decisions, related to therapeutic advantages and disadvantages.
Declarations
Conflict of Interests
Not applicable.
Funding
This study did not receive financial support from public, commercial or non-profit sources.
References
- Nourian A, Dhaliwal S, Vangala S, Vezeridis PS. (2017). Midshaft Fractures of The Clavicle: A Goal- Analysis Comparing Surgical Fixation Using Anteroinferior Plating Versus Superior Plating. J Orthop Trauma. 31(9):461-467.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Canadian Orthopedic Trauma Society. (2007). Nonoperative Treatment Compared with Plate Fixation of Displaced Midshaft Clavicular Fractures. A Multicenter, Randomized Clinical Trial. J Cap Joint Surg Am. 89(1):1-10.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Woltz S, Stegeman SA, Krijnen P, et al. (2017). Plate Fixation Compared with Nonoperative Treatment for Displaced Midshaft Clavicular Fractures: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. J Cap Joint Surg Am. 99(2):106-112.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Robinson CM, Goudie E.B., Murray GO, et al. (2013). Open Reduction and Plate Fixation Versus Nonoperative Treatment for Displaced Midshaft Clavicular Fractures: A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Trial. J Cap Joint Surg Am. 95(17):1576-1584.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, et al. (2009). The PRISM Statement for Reporting Systematically Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies that Evaluate Health Care Interventions: Explanation and Elaboration. PLoS Med, 6(7):e1000100.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Booth A. (2016). Searching For Qualitative Research for Inclusion in Systematic Reviews: A Structured Methodological Review. Syst Rev, 5(1):74.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Virtanen KJ, Remes V, Pajarinen J, Savolainen V, Björkenheim JM, et al. (2012). Sling Compared with Plate Osteosynthesis for Treatment of Displaced Midshaft Clavicular Fractures: The Randomized Clinical Trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 94(17):1546-1553.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Robinson CM, Goudie EB, Murray GO, Jenkins PJ, Ahktar BAD, et al. (2013). Open Reduction and Plate Fixation Versus Nonoperative Treatment for Displaced Midshaft Clavicular Fractures: A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 95(17):1576-1584.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Melean PA, Zuniga A, Marsalli M, Fritis NA, Cook ER, et al. (2015). Surgical Treatment of Displaced Middle-Third Clavicular Fractures: A Prospective, Randomized Trial in A Working Compensation Population. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 24(4):587-592.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Woltz S, Stegeman SA, Krijnen P, van Dijkman BA, van Thiel TP, et al. (2017). Plate Fixation Compared with Nonoperative Treatment for Displaced Midshaft Clavicular Fractures: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. J Cap Joint Surg Am. 99(2):106-112.
Publisher | Google Scholor - WANG, Jia et al. (2015). Interventions for Treating Displaced Midshaft Clavicular Fractures: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Medicine, 94(11):e595.
Publisher | Google Scholor - WANG, Xin-Hua et al. (2015). Operative Versus Nonoperative Treatment for Displaced Midshaft Clavicle Fractures: The Meta-Analysis Based on Current Evidence. Clinics, 70:584-592.
Publisher | Google Scholor - WOLTZ, Sarah; KRIJNEN, Pieta; SCHIPPER, Inger B. (2017). Plate Fixation Versus Nonoperative Treatment for Displaced Midshaft Clavicular Fractures: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. JBJS, 99(12):1051-1057.
Publisher | Google Scholor - AXELROD, Daniel E. et al. (2020). What is the Best Evidence for Managing Displacement Midshaft Clavicle Fractures? A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis Of 22 Randomized Controlled Trials. Clinical Orthopedics and Related Research®, 478(2):392-402.
Publisher | Google Scholor - WOLTZ, Sarah; KRIJNEN, Pieta; SCHIPPER, Inger B. (2017). Plate Fixation Versus Nonoperative Treatment for Displaced Midshaft Clavicular Fractures: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. JBJS, 99(12):1051-1057.
Publisher | Google Scholor - SCHLÜßLER, Antonia et al. (2023). Biomechanical And Clinical Evaluation of Minimal Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis for Two-Part Clavicle Shaft Fractures. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 24(1):612.
Publisher | Google Scholor - Zhu, Yurun et al. (2023). Refracture After Plate Removal of Midshaft Clavicle Fractures After Cap Union-Incidence, Risk Factors, Management and Outcomes. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 24(1):308.
Publisher | Google Scholor